Verarbeitungstätigkeit/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Weitere Optionen
Faha (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
Isan (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| Zeile 187: | Zeile 187: | ||
<b>Impact assessment</b> | <b>Impact assessment</b> | ||
* This shows whether a data protection impact assessment has been completed for the current processing activity. | * This shows whether a data protection impact assessment has been completed for the current processing activity and if so, what its state is. The result of the data protection impact assessment can also dictate that the processing activity may no longer be carried out due to its not being aligned with the data protection regulations. | ||
: The following states for the DPIA are possible: | |||
:*No assessment performed → no DPIA is linked to the PA. | |||
:*DPIA necessary → DPIA linked, but no result available yet. | |||
:*DPIA not necessary → DPIA linked and deemed not necessary. | |||
:*DPIA attached → DPIA linked, file attached, but no result available yet. | |||
:*PA approved → DPIA available and as a result the PA may be carried out. | |||
:*PA with stipulation → DPIA available and as a result the PA may only be carried out after the stipulations (measures/controls) have been implemented. | |||
:*PA prohibited → DPIA available and as a result the PA may not be carried out because it goes against the data protection regulations. | |||
You can find more information about data protection impact assessments in [[Special:MyLanguage/Datenschutz-Folgenabschätzung|"Data protection → DPIA"]]. | |||
Version vom 27. September 2022, 09:52 Uhr
What is a processing activity?
- A legal definition of the term can be found in Art. 4 of the GDPR, where "processing activity" is defined as follows:
- any operation or set of operations which is performed on personal data or on sets of personal data, whether or not by automated means.
- This means a processing activity is any process or procedure in which any form of personal data is processed, whether it is simply saved or used for evaluation.
Processing activity details
Now, the individual parts of the processing activity will be described.
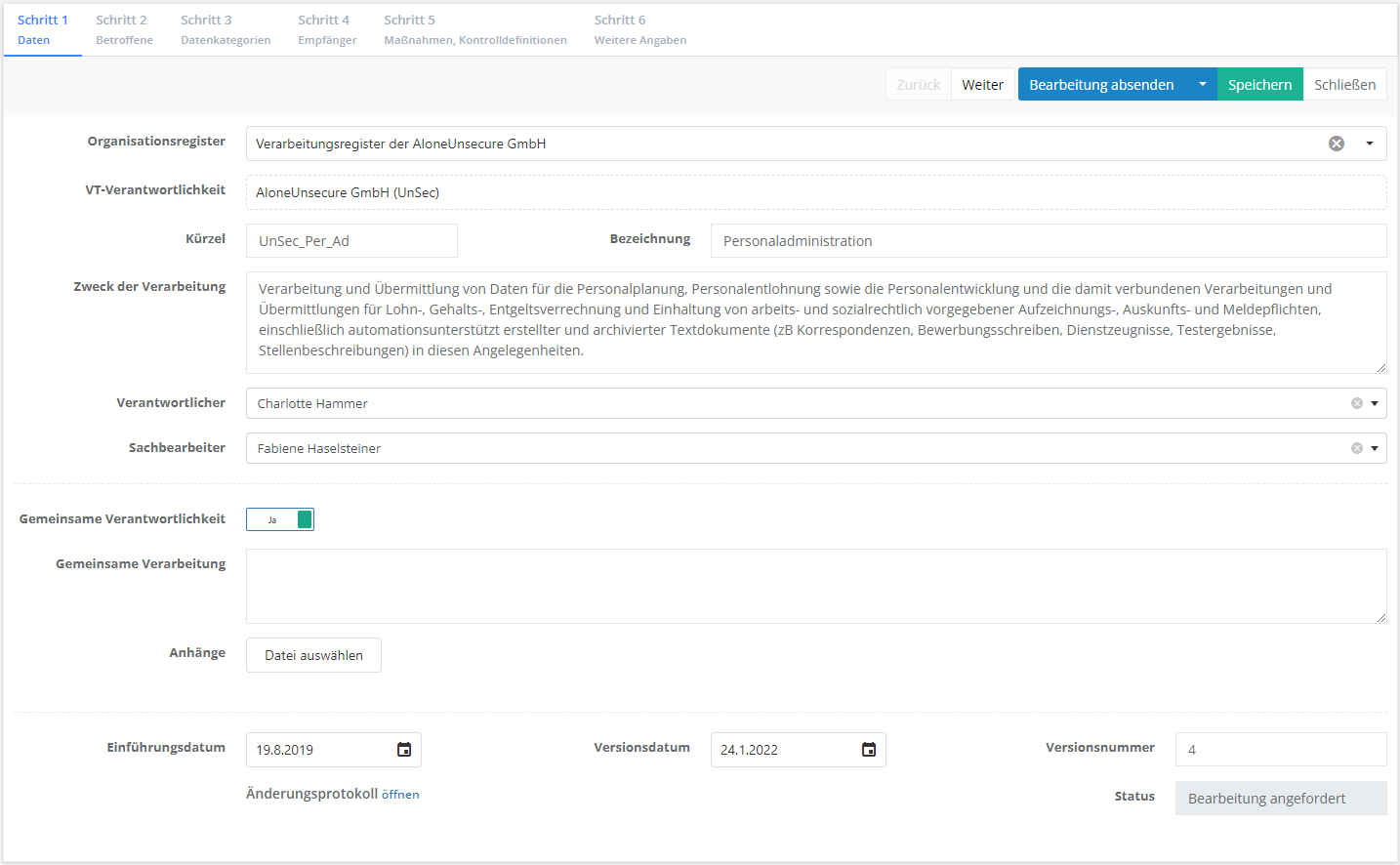
Organizational register:
- Here, name the register responsible for the processing activity.
PA-responsibility:
- Here, designate one or more persons responsible, who decide over the means and purpose of the processing of the personal data. For this, enter the organizational units or external persons responsible for the processing activity. In the mapping dialog, only those contacts created in "Data protection → Externals" are displayed, which have also been marked as PA-responsible. This label needs to be set directly in the External creation mask ("Data protection → Externals"). If the respective external has not yet been created, this can be done directly here.
Code and Name:
- Here, assign a code and a name for the PA.
Purpose of the processing activity:
- Here, the purpose of the processing of the personal data must be recorded.
Person responsible:
- The person or team responsible for the PA within the company.
Advisor:
- This is the person or team tasked with editing the processing activity.
Joint responsibility:
- If two or more responsibles together decide the purposes and means of a processing activity, they share joint responsibility. In a transparent agreement, they stipulate which of them fulfills which one of the obligations according to the ordinance, especially regarding the rights of the data subjects, and who complies with information obligation in accordance with Articles 13 and 14.
- There should also be a short description of who fulfills which obligations according to the ordinance.
- Agreements and any other relevant documents created for this purpose can be uploaded here.
Implementation date:
- Set the date the processing activity becomes valid.
Version date:
- Set the date the current version of the processing activity becomes valid.
Version number:
- This displays which version of the processing activity is currently active.
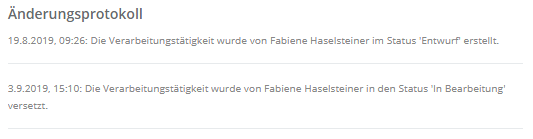
Change log:
- Here, the time and author of changes made to the processing activity, the time of a status change, and the time of its completion are recorded.
Status and deletion of a processing activity
A processing activity can be in various states. If e-mail notifications are activated in the management system, all relevant people in the workflow are prompted to perform their respective tasks when the state is changed. In this case, it would be the advisor, if an expert of professional requests the editing of a processing activity.
Draft
- The first time a processing activity is saved or when it is deactivated while in the state "In editing", it is moved into the state "Draft". From here, it can be activated, as in moved into the state "In editing".
In editing
- When a processing activity is activated, it is moved into the state "In editing". It is now time for an expert or a responsible professional to perform the processing activity or to request performance from an advisor by selecting "Request editing".
- It can be moved back into the state "Draft" by selecting "Deactivate editing".
- It can be moved into the state "Editing completed" by selecting "Complete editing".
Editing requested
- When a processing activity is requested, it is moved into the state "Editing requested". The advisor is now prompted via e-mail to edit the processing activity.
- It can be moved into the state "Answered" by selecting "Submit edits".
Answered
- When a processing activity is returned by the advisor via the option "Submit edits", it is moved into the state "Answered".
- It can be moved back into the state "Editing requested" by selecting "Request editing" again and the advisor will have to revise their edits.
- It can be returned into the state "Draft" by selecting "Deactivate editing".
- It can be moved into the state "Editing completed" by selecting "Complete editing".
Editing completed
- When a processing activity is moved into the state "Editing completed" by selecting "Commplete editing", it is turned read-only and can no longer be edited.
- When the processing activity moves into this state, a process is created automatically for this processing activity. Processes are accessible to experts in "Administration → Processes".
Deleting and annulling a processing activity
- By selecting "Delete processing activity", a processing activity can be deleted so long as it has not been completed.
- Caution: Because of their historicization, completed processing activities can no longer be deleted! They can merely be annulled by selecting the Button "Annul processing activity" in the overview found in "Data protection → Processing registers → Processing activities".
- Annulled processing activities can no longer be activated!
Add data subjects
In this tab, an expert, a responsible professional or an advisor can add data subjects ot the processing activity.
Data subject categories can be created and administrated by experts in "Data protection → Data subject categories". Find more here.
Clicking on "Assign existing data subject categories" opens a dialog in which you can choose which data subject categories are to be assigned to the processing activity. Here, choose all data subject categories whose personal data are processed in the processing activity.
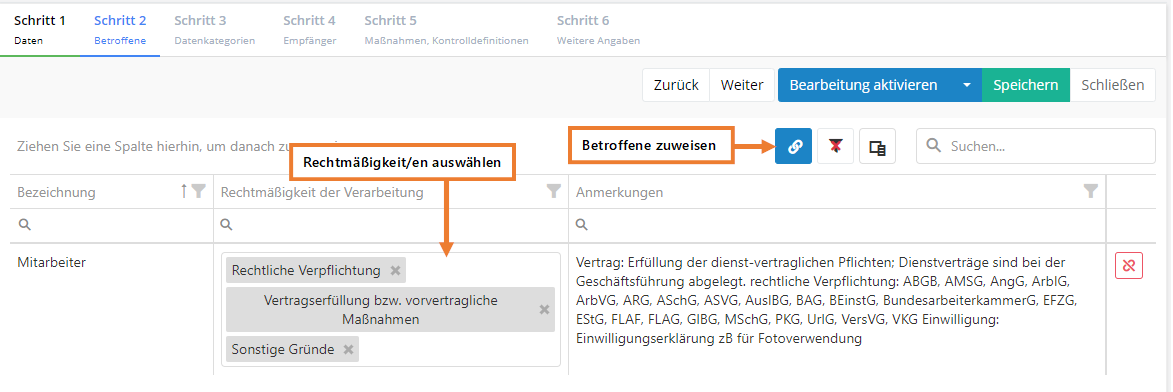
Important:
For every data subject category the legal basis of the processing has to be stated in accordance with Article 6 GDPR Lawfulness of processing. For this, the column "Legitimacy of the processing" offers the following reasons to choose from:
- Consent to processing by data subject
- Vital interests
- Legal obligation
- Performance of the contract or pre-contractual measures
- In the public interest or in the exercise of official authority
- Legitimate interests of the responsible person or a third party
- Other reasons (GDPR: legally not justified)
- This option mainly serves as a placeholder in case the legitimacy is unclear at the time of creating the processing activity! It is by no means avalid legal basis in accordance with Art. 6 GDPR. Therefore, it should not appear in the finished PA but be replaced with a valid legal basis!
It is possible to select multiple legal bases for the processing.
Add data categories
In this tab, an expert, a responsible professional, or an advisor adds the personal data categories to the respective data subject categories. Only those data categories are available that have been marked as "personal".
Data categories can be created and administrated by experts in "Administration → Data categories". Find more here.
About the table:
- This table contains input fields that can be filled in.
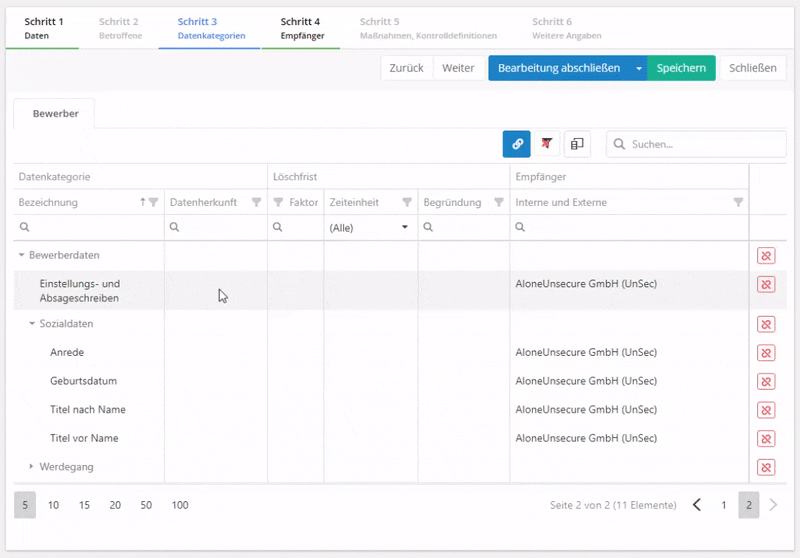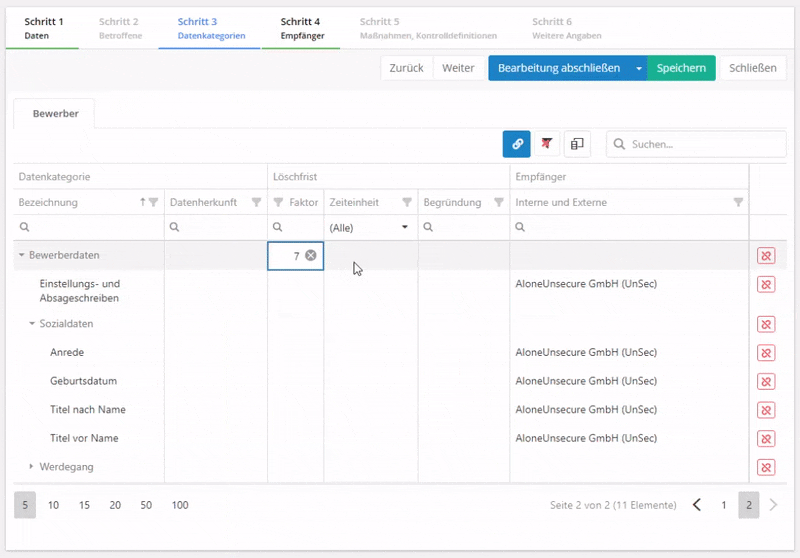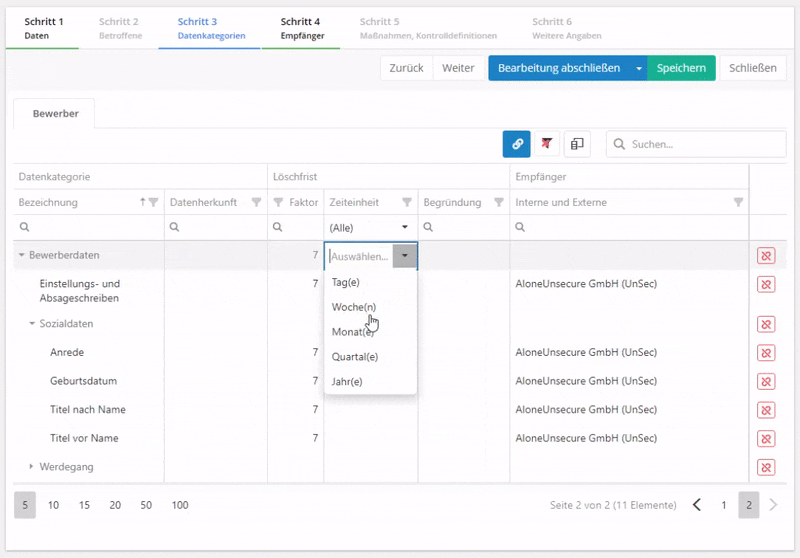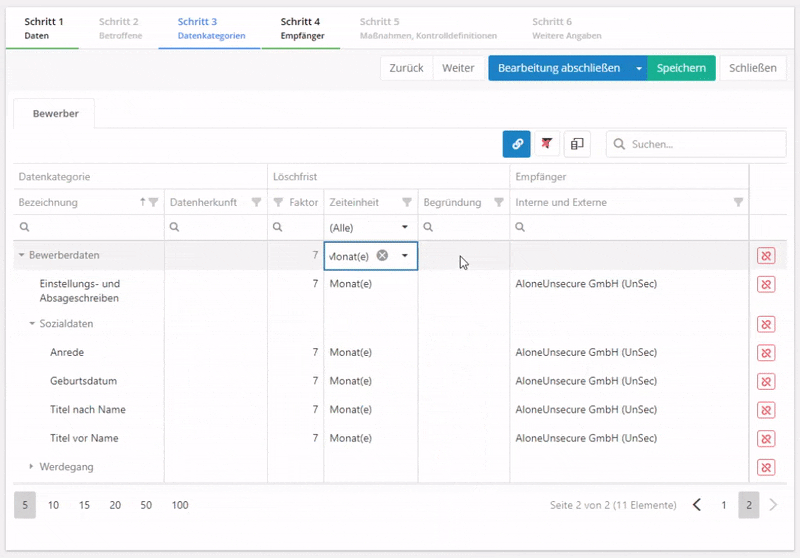
- The data categories are displayed hierarchically. Any information entered for a superordinate data category is applied to all subordinate data categories. Example: If the value 7 is entered in the field "Time limit for erasure → Factor", this value is forwarded to all subordinate data categories.
- If a time limit for erasure is set for a data category, it is applied automatically. If it does not fit the PA, it can be changed here without issue.
Caution:
- Assigning new recipients in the superordinate data category does not replace the existing allocations but supplements them. Example: If recipient A has already been assigned to the subordinate data categories and recipient B is assigned to the superordinate data category, then the subordinate data categories are assigned recipient B in addition to recipient A.
Assign/transfer data category
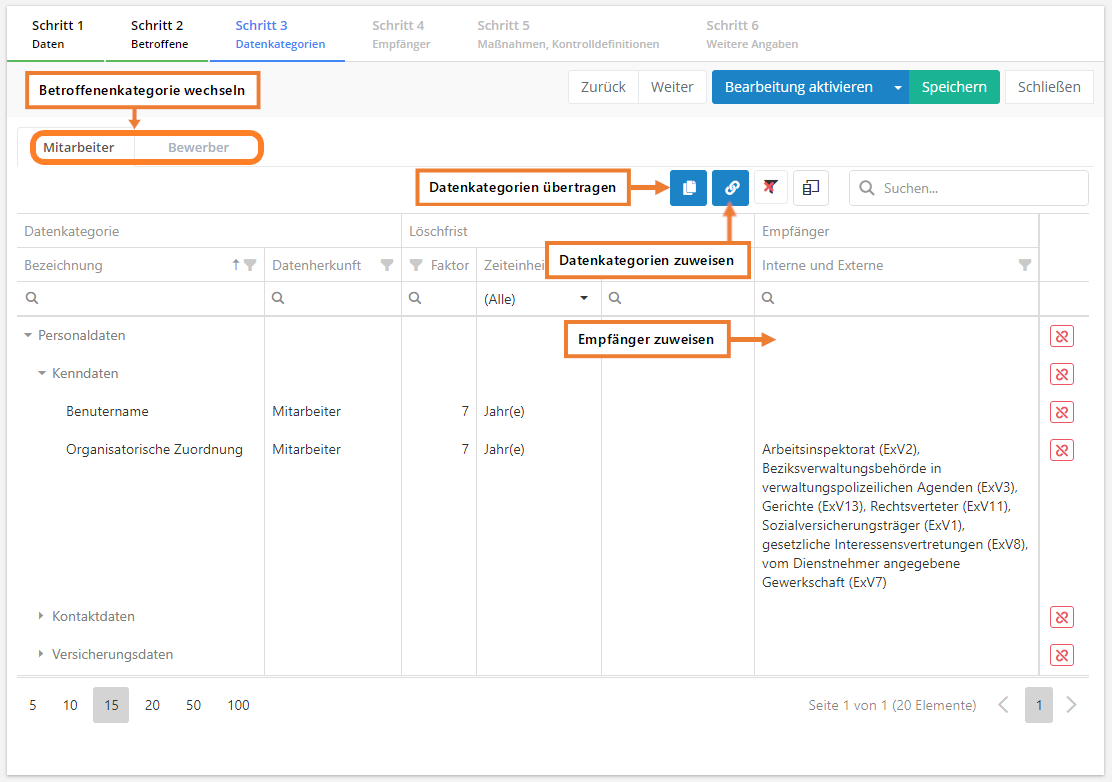
Assign data categories
Data categories are assigned as follows:
- Selecting "Assign existing data categories" opens a dialog in which the data category is added to the data subject category. These are the categories of data processed in the processing activity.
- Source of data: this shows where the data originates.
- Time limit for erasure: this specifies after which amount of time data must be deleted. Also, the deletion period must be justified, i.e. by referring to legal obligations to preserve records.
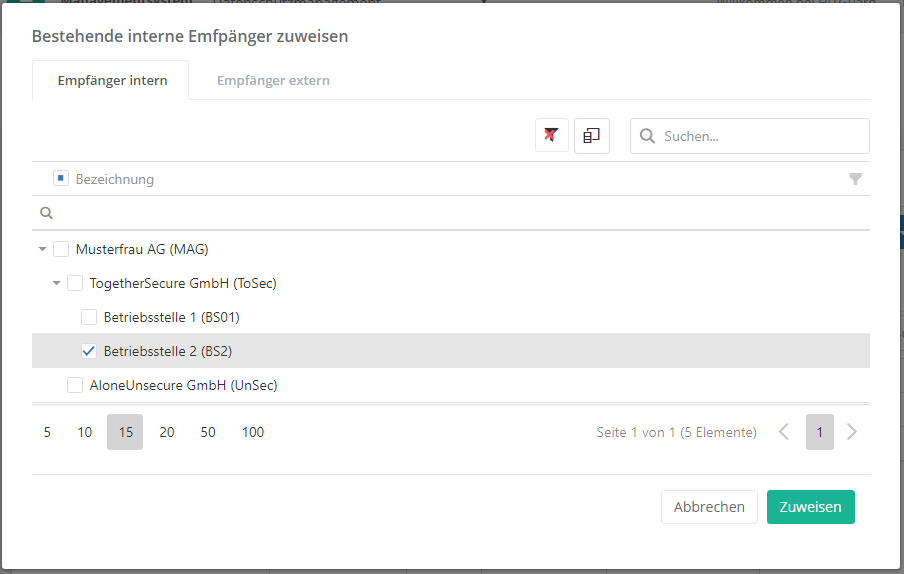
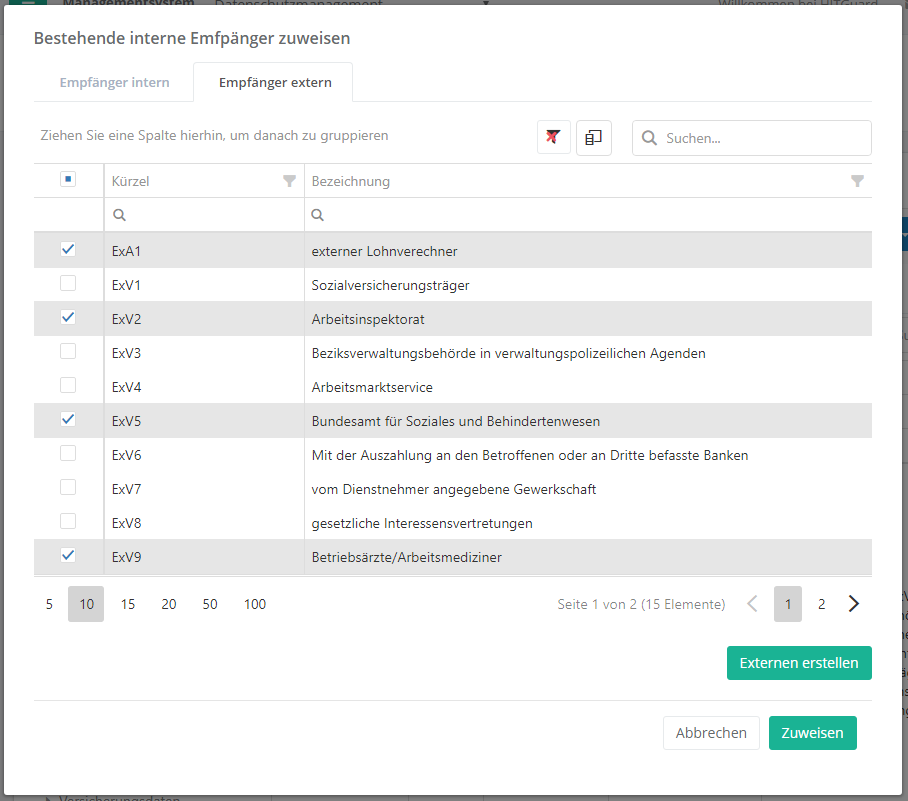
- Recipient: this states who receives the personal data. A distinction is made between internal and external recipients. Internal recipients are the company's organizational units. External recipients include banks, the unemployment office, courts, authorities, etc. In order to add a recipient, double-click into an empty recipient field. This opens a dialog in which internal and external recipients can be selected.
- It must be ensured that all data subject categories are dealt with! (It is possible to navigate to the data subject categories via the tabs at the top.)
Transfer data categories
If a PA affects multiple data subject categories, it is likely that the same data categories are processed for each of them. In order to avoid having to assign and configure the data categories separately for each data subject category, there is an option to "Transfer assigned data categories". This button copies all current data categories with their respective configurations to the selected data subject categories.
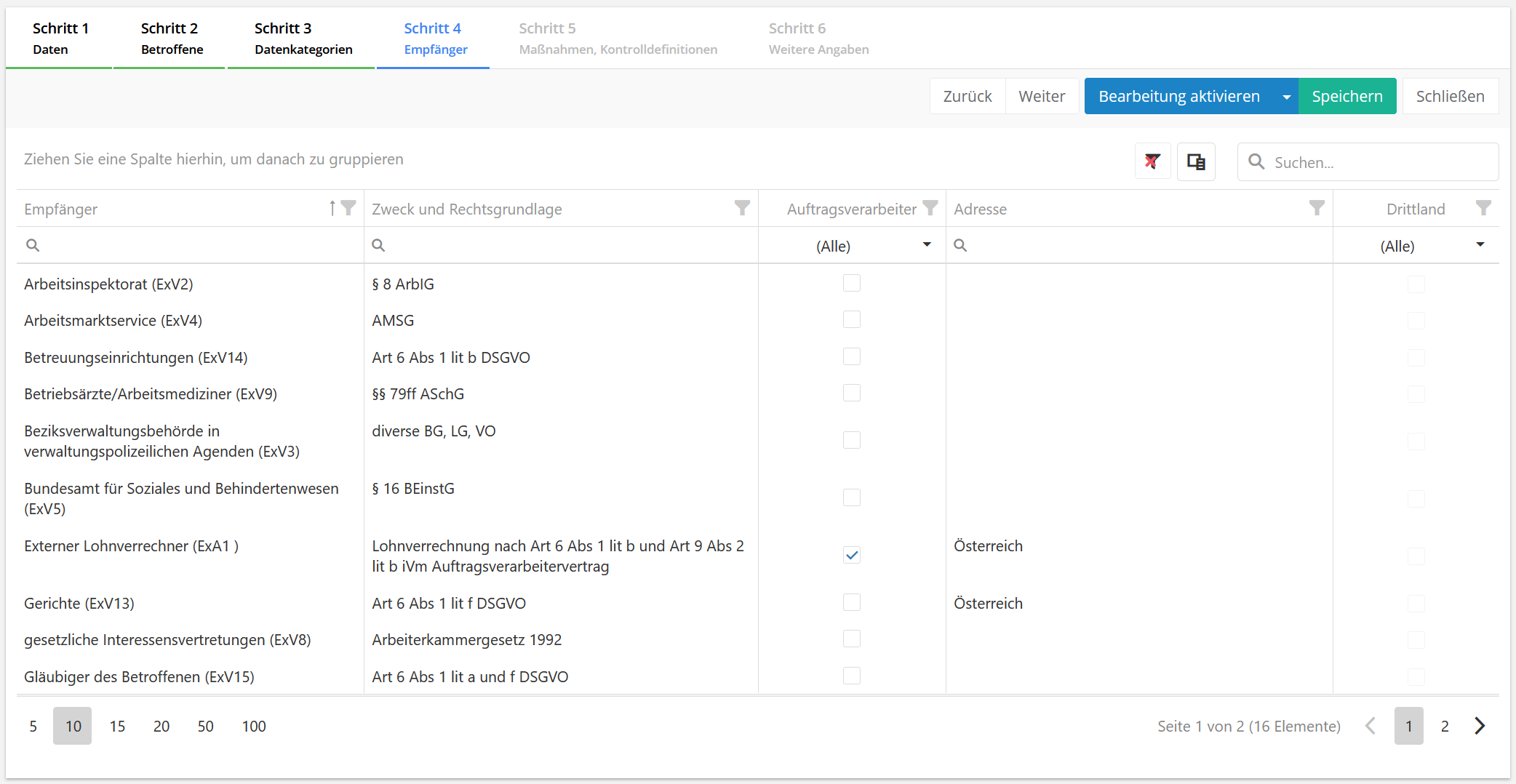
Overview of recipients
In this tab, all recipients assigned to a data category are listed. It is recorded what the purpose of a transfer of personal data to a recipient is and what legal basis the transfer is based on. Furthermore, it can be recorded whether the recipient is also a data processor.
Purpose and legal basis are recorded via an input field in this table.
Assign measures and control definitions
In this tab, technical and organizational measures and controls can be assigned to the specific processing activity. If a technical or organizational measure or control applies to all processing activities, it must be added to the general technical and organizational measures in "Data protection → TOMs". Find more on this here.

Further details
In this tab, further details about the processing activity are recorded.
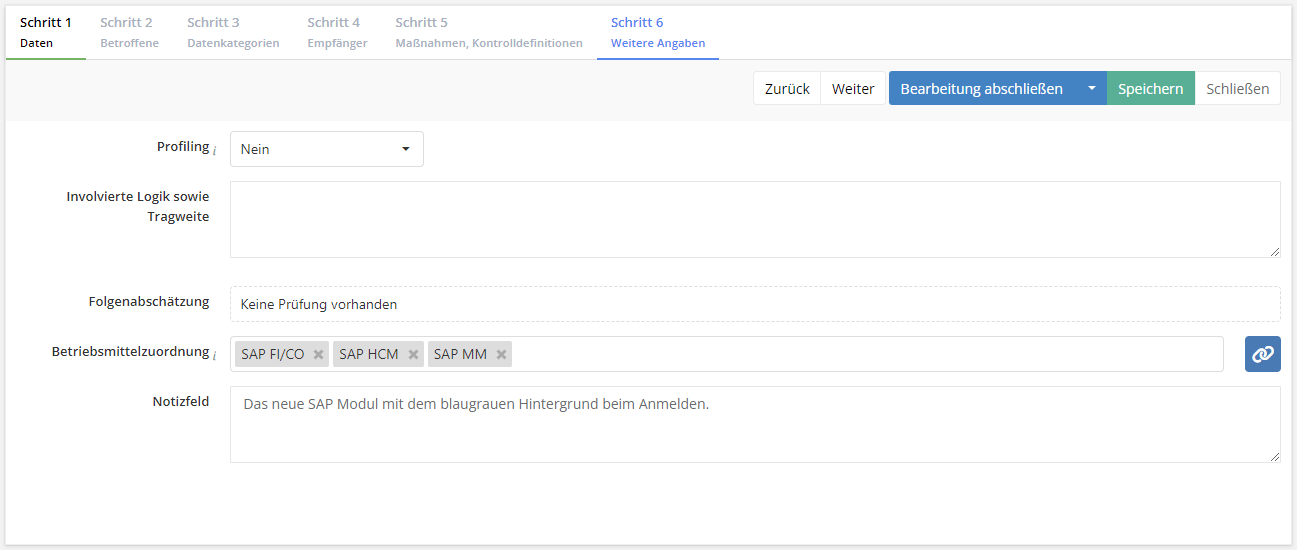
Profiling
- Profiling, according to the GDPR, is any form of automated processing of personal data evaluating the personal aspects relating to a natural person, in particular to analyse or predict aspects concerning the data subject’s performance at work, economic situation, health, personal preferences or interests, reliability or behaviour, location or movements.
- If the processing of personal data constitutes any kind of profiling, "Yes" must be selected here and profiling activity's involved logic and implications must be described. This is important as it must be recognizable in a notification of a processing activity whether profiling is involved or not!
Impact assessment
- This shows whether a data protection impact assessment has been completed for the current processing activity and if so, what its state is. The result of the data protection impact assessment can also dictate that the processing activity may no longer be carried out due to its not being aligned with the data protection regulations.
- The following states for the DPIA are possible:
- No assessment performed → no DPIA is linked to the PA.
- DPIA necessary → DPIA linked, but no result available yet.
- DPIA not necessary → DPIA linked and deemed not necessary.
- DPIA attached → DPIA linked, file attached, but no result available yet.
- PA approved → DPIA available and as a result the PA may be carried out.
- PA with stipulation → DPIA available and as a result the PA may only be carried out after the stipulations (measures/controls) have been implemented.
- PA prohibited → DPIA available and as a result the PA may not be carried out because it goes against the data protection regulations.
You can find more information about data protection impact assessments in "Data protection → DPIA".