Workflow Kontrolle/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Weitere Optionen
Isan (Diskussion | Beiträge) Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „Workflow control“ |
Isan (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| Zeile 3: | Zeile 3: | ||
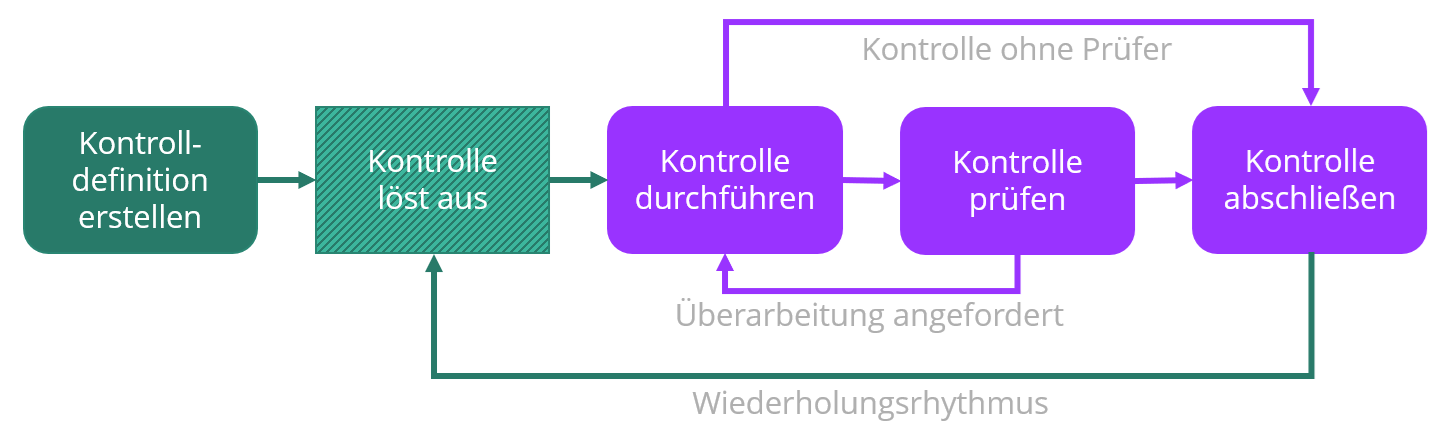
A control definition is the basis of a usually repeating task, which is created in HITGuard and assigned an implementer for execution and an examiner for review. A control is the task that triggers based on the repetition rhythm and that is executed and reviewed. | A control definition is the basis of a usually repeating task, which is created in HITGuard and assigned an implementer for execution and an examiner for review. A control is the task that triggers based on the repetition rhythm and that is executed and reviewed. | ||
====How can a control definition be created?==== | ====How can a control definition be created?==== | ||
Experts and Professionals can freely create control definitions, create them in the course of interviews for reviews, create them directly out of a risk or opportunity for its treatment, or create them in the context of a case management dossier. Experts and Professionals can decide between freely creating a control definition or creating it from a knowledge base template.<p>It is determined for each control, in which rhythm it repeats. | Experts and Professionals can freely create control definitions, create them in the course of interviews for reviews, create them directly out of a risk or opportunity for its treatment, or create them in the context of a case management dossier. Experts and Professionals can decide between freely creating a control definition or creating it from a knowledge base template.<p>It is determined for each control, in which rhythm it repeats. | ||
====How are controls executed?==== | ====How are controls executed?==== | ||
| Zeile 13: | Zeile 11: | ||
====How are controls examined?==== | ====How are controls examined?==== | ||
If one of more examiner are configured in the control, they receive an e-mail when the control is ready for review. They inspect the execution description and any evidences and decide whether they are in order. If so, they accept the control. If not, they can request a reworking or reject the control. | If one of more examiner are configured in the control, they receive an e-mail when the control is ready for review. They inspect the execution description and any evidences and decide whether they are in order. If so, they accept the control. If not, they can request a reworking or reject the control. | ||
<div lang="de" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> | |||
====Wer bekommt wann ein E-Mail?==== | |||
<b>Umsetzer:</b> | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn auf Basis der Kontrolldefinition eine Kontrolle ausgelöst wurde, die nun von ihm durchzuführen ist. | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn seine Bearbeitung nicht mehr notwendig ist (z.B. ein anderer Umsetzer hat durchgeführt). | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn seine Bearbeitung nochmals gefragt ist (z.B. der Prüfer hat eine Überarbeitung angefordert). | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn eine Erinnerung eingestellt wurde und verschickt wird. | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn die Kontrolle fehlgeschlagen ist. | |||
<b>Prüfer:</b> | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn der Umsetzer die Kontrolle zur Prüfung freigibt. | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn seine Bearbeitung nicht mehr notwendig ist (z.B. ein anderer Prüfer hat geprüft). | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn eine Erinnerung eingestellt wurde und auch an den Prüfer verschickt wird. | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn die Kontrolle fehlgeschlagen ist. | |||
<b>Funktionale Eskalation:</b> | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn ein Schwellwert eingestellt und dieser erreicht wurde. | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn die Deadline der Kontrolle überschritten wurde. | |||
<b>Managementsystemverantwortlicher:</b> | |||
*Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn ein Schwellwert eingestellt und dieser erreicht wurde. | |||
</div> | |||
====Additional links==== | ====Additional links==== | ||
Version vom 3. Februar 2025, 11:39 Uhr
What is a control?
A control definition is the basis of a usually repeating task, which is created in HITGuard and assigned an implementer for execution and an examiner for review. A control is the task that triggers based on the repetition rhythm and that is executed and reviewed.
How can a control definition be created?
Experts and Professionals can freely create control definitions, create them in the course of interviews for reviews, create them directly out of a risk or opportunity for its treatment, or create them in the context of a case management dossier. Experts and Professionals can decide between freely creating a control definition or creating it from a knowledge base template.
It is determined for each control, in which rhythm it repeats.
How are controls executed?
Implementers receive an e-mail when the control triggers. They execute the control measure and fill in the execution description. Optionally, they can leave a remark and upload evidences. Then the control is forwarded to the examiners for review or closed, if no examiner was configured.
How are controls examined?
If one of more examiner are configured in the control, they receive an e-mail when the control is ready for review. They inspect the execution description and any evidences and decide whether they are in order. If so, they accept the control. If not, they can request a reworking or reject the control.
Wer bekommt wann ein E-Mail?
Umsetzer:
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn auf Basis der Kontrolldefinition eine Kontrolle ausgelöst wurde, die nun von ihm durchzuführen ist.
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn seine Bearbeitung nicht mehr notwendig ist (z.B. ein anderer Umsetzer hat durchgeführt).
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn seine Bearbeitung nochmals gefragt ist (z.B. der Prüfer hat eine Überarbeitung angefordert).
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn eine Erinnerung eingestellt wurde und verschickt wird.
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn die Kontrolle fehlgeschlagen ist.
Prüfer:
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn der Umsetzer die Kontrolle zur Prüfung freigibt.
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn seine Bearbeitung nicht mehr notwendig ist (z.B. ein anderer Prüfer hat geprüft).
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn eine Erinnerung eingestellt wurde und auch an den Prüfer verschickt wird.
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn die Kontrolle fehlgeschlagen ist.
Funktionale Eskalation:
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn ein Schwellwert eingestellt und dieser erreicht wurde.
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn die Deadline der Kontrolle überschritten wurde.
Managementsystemverantwortlicher:
- Bekommt ein E-Mail, wenn ein Schwellwert eingestellt und dieser erreicht wurde.
Additional links
Find more on the creation of control definitions for Experts and Practitioners here.
Find more on the execution of controls for Practitioners here.
Find more on the review of controls for Practitioners here.