Erstellen einer Wissensdatenbank/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Weitere Optionen
Isan (Diskussion | Beiträge) Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „*<u>Numbering and title:</u><br> :: The numbering should be logical and comprehensible.<br> The title should be informative, so the user immediately knows what…“ |
Isan (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| Zeile 121: | Zeile 121: | ||
:: Pose a clearly formulated question here. | :: Pose a clearly formulated question here. | ||
*<u> | *<u>Description:</u><br> | ||
:: If necessary, further describe the question here. For example, you might describe the basic conditions that need to be fulfilled for a question to be answered positively. | :: If necessary, further describe the question here. For example, you might describe the basic conditions that need to be fulfilled for a question to be answered positively. | ||
Version vom 30. Juni 2022, 08:53 Uhr
TogetherSecure creates and provides knowledge bases. Also, any user with the expert role in risk management is able to create a new knowledge base or modify an existing one. In other words, a a knowledge base can be created or changed by any expert.
This means, experts can add and hierarchically sort topics. Topics are then assigned review questions, either newly created or from an existing pool of questions. In the next step, threats, justification templates, measures, and/or controls can be created or assigned from existing ones. If, for example, a knowledge base already includes measures and controls (as is the case with BSI IT-Grundschutz), that means appropriate measures and controls have already been thought up for the offered threats. Users are encouraged, however, to evaluate their respective scenarios and create additional measures and/or controls for the treatment of the threats.
Create/edit knowledge base
To create or edit a knowledge base, navigate to "Administration → Knowledge bases".
Here, all knowledge bases are listed, whether they have been published or not. Only published knowledge bases can be used for reviews. Published knowledge bases are marked with a green tick. If there are multiple versions of a knowledge base, one can be declared the default version (see: edit). It is then marked with a red heart.
create:
- To create a new knowledge base, click the "Create new knowledge base" button. Then, enter the header information, create topics and their review questions, and finally assign measures, controls, justification templates, and threats.
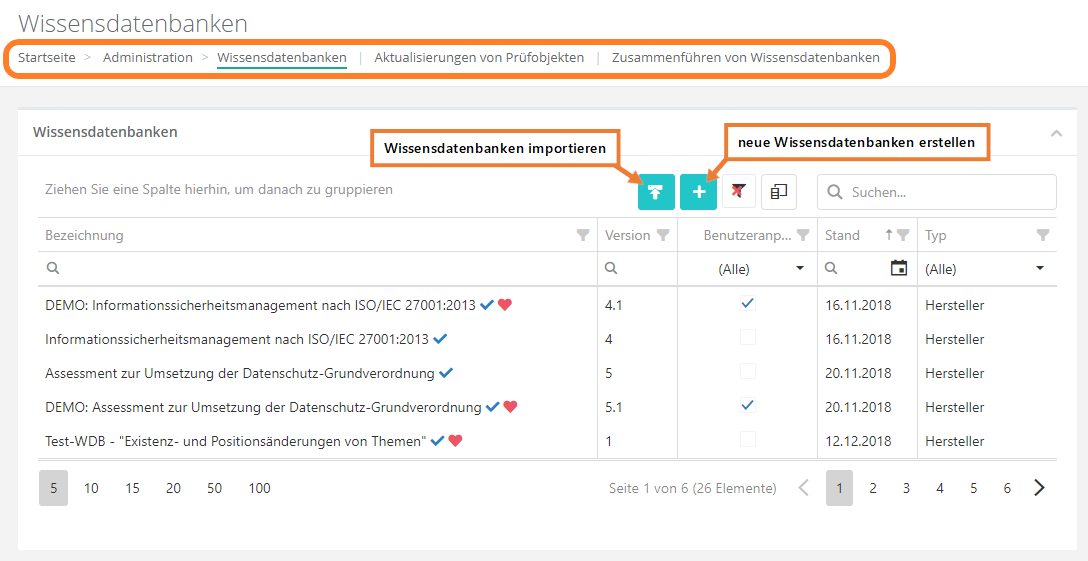
edit:
- To edit a KB, click on the desired KB. Published knowledge bases are read-only and can therefore no longer be modified. If a KB has been published, you need to create a superseding version or a user adaptation (of a vendor knowledge base). In the same interface, you can also set a KB as the default version if multiple versions of the KB exist.
- The superseding version is unpublished and can therefore be edited.
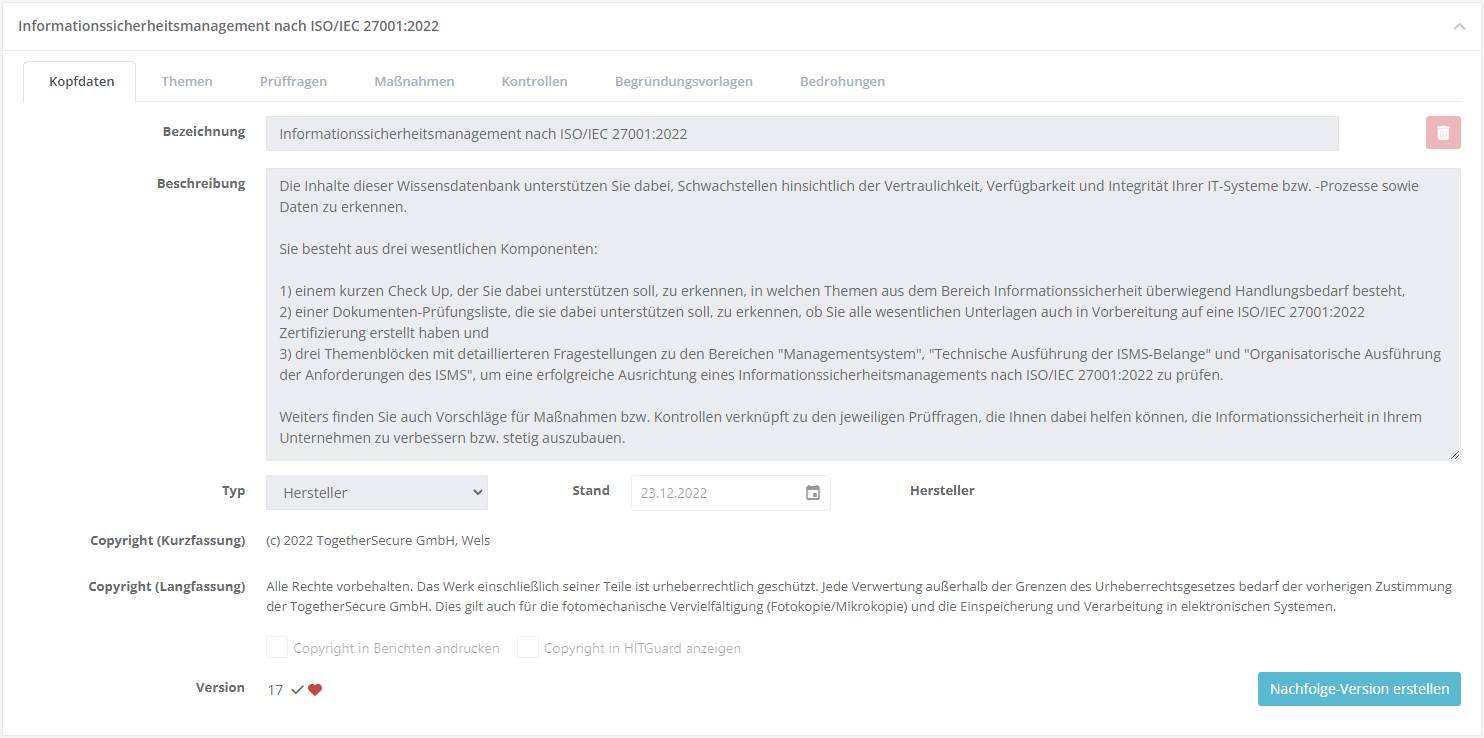
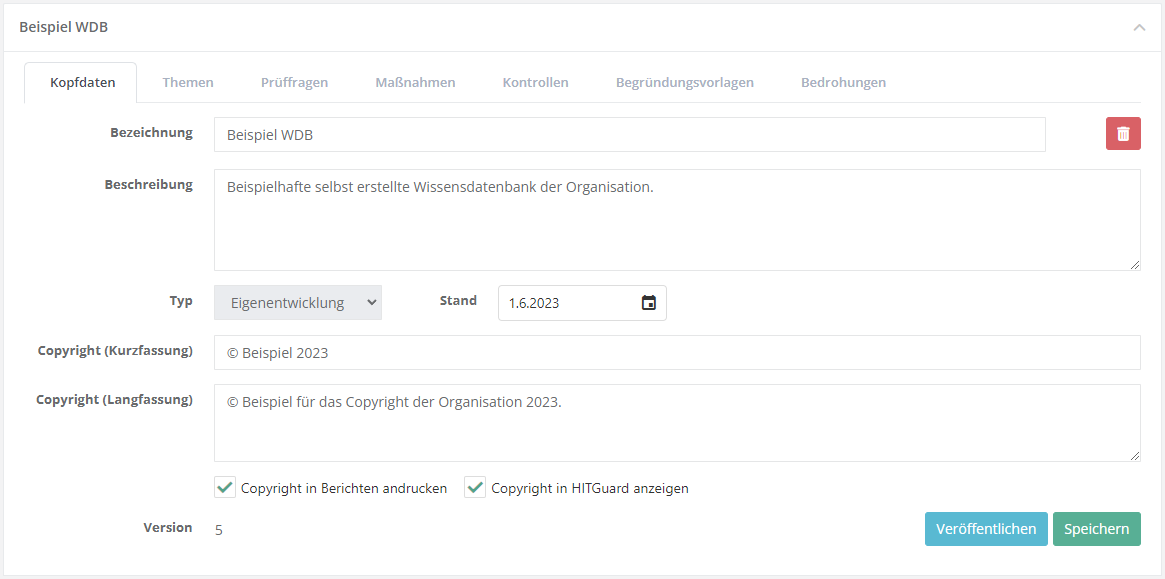
Header information
In the header data, briefly describe the purpose of the knowledge base. Depending on whether it is a self developed knowledge base or one for a norm, you need to set the type accordingly, set the effective date, and add the creator (e.g. name or company). Caution: only KBs of the types vendor or norm or standard can be exported. Additionally, you can add a copyright note. This copyright note is then displayed with every measure, control, and review question of the knowledge base (also in reports).
Type vendor and norm or standard
To create KBs of the type vendor or norm or standard, you need to have a vendor license! These KBs are also the only ones that can be exported.
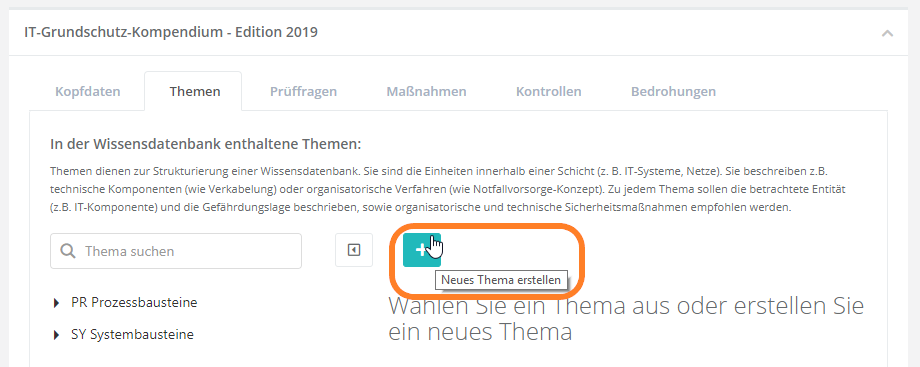
Topics
Here, all the topics that are part of the KB are listed hierarchically. The purpose of topics is to give knowledge bases a meaningful structure.
Create/edit topic
To create a new topic, navigate to the tab "Topics" and click on "create new topic". Then fill out the displayed form.
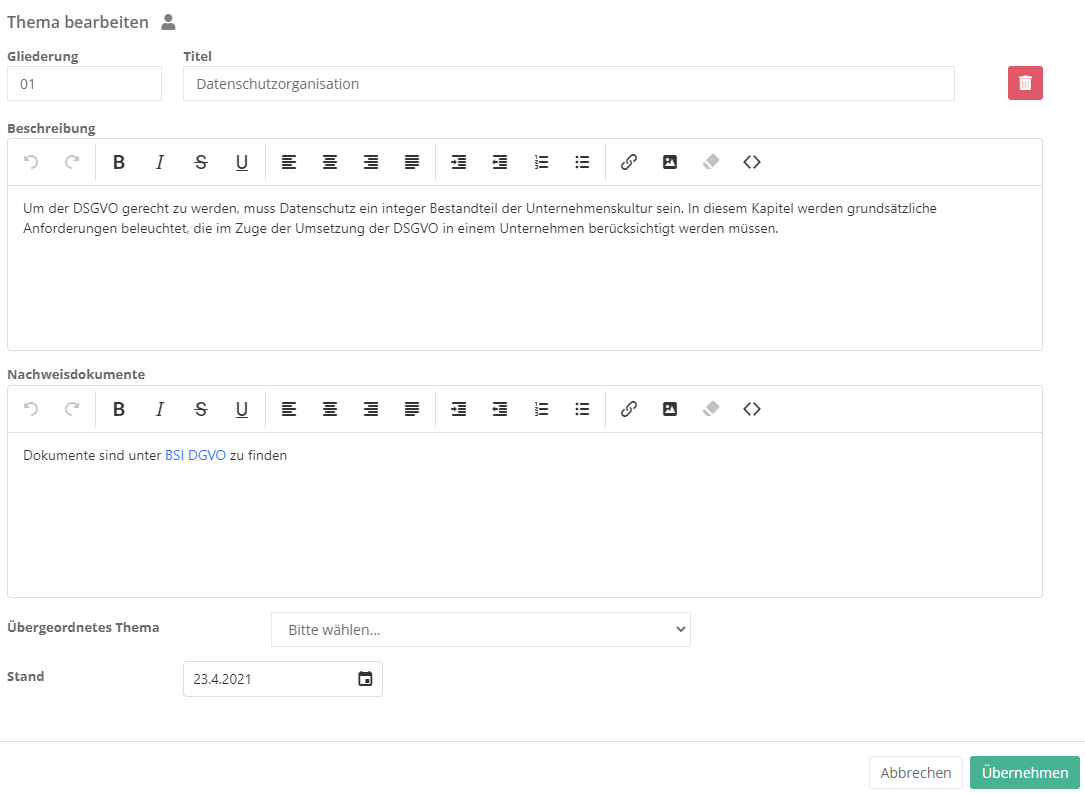
- Numbering and title:
- Here, set the numbering and the title. The numbering should help clarify the KB's structure, e.g. 1, 1.1, 1.2, etc. The title should be informative, so the user immediately knows what questions the topic covers.
- Description:
- Here, describe the purpose of the topic. This text field supports HTML formatting.
- Supporting documents:
- Here, record references or links to documents that might be relevant for the preparation of auditing this topic.
- Parent topic:
- If the topic is a subordinate one, the parent topic has to be set here so the KB is structured properly.
NO TRANSLATION
NO TRANSLATION
- Effective date:
- This should be the date of the latest revision.
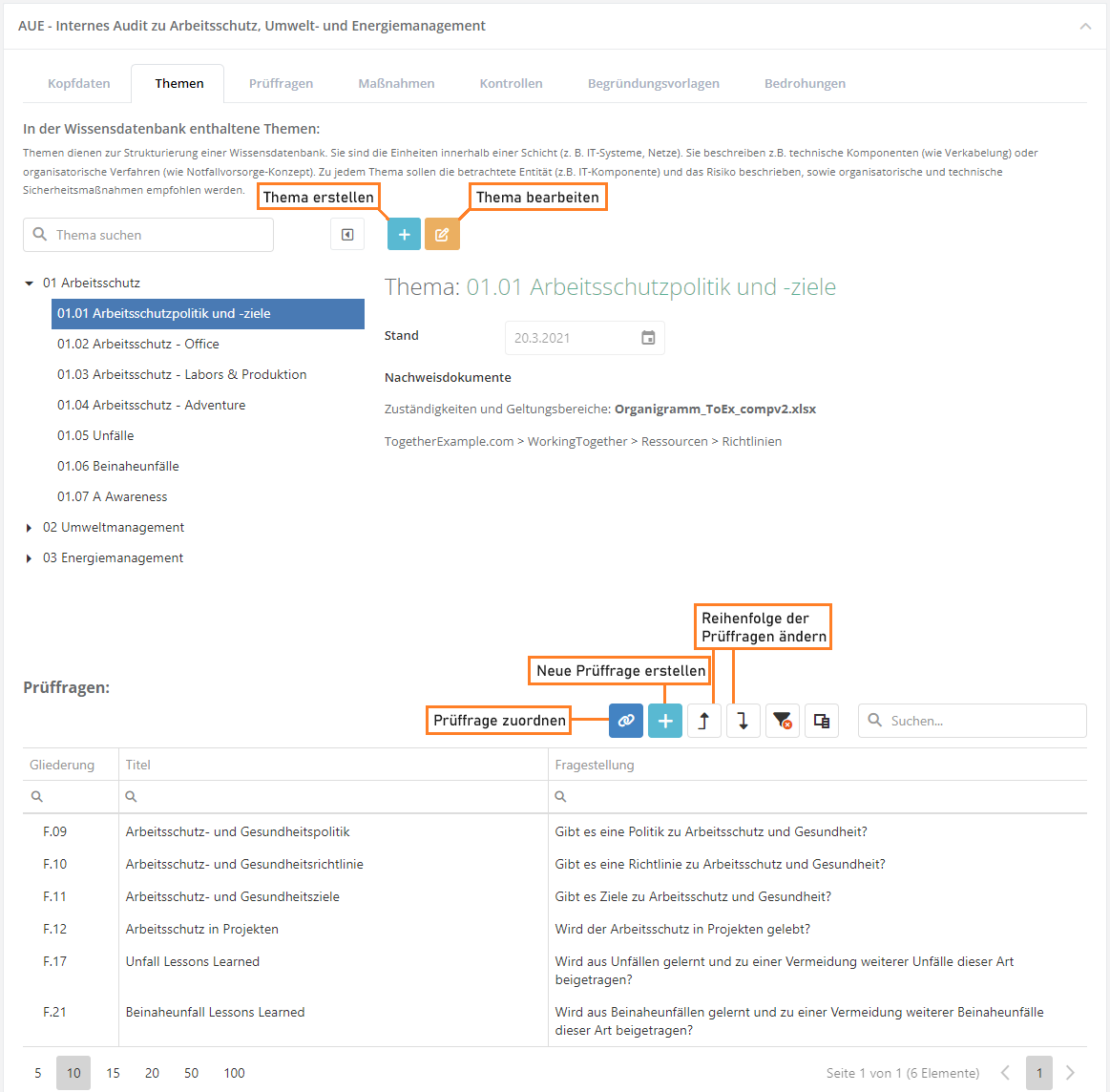
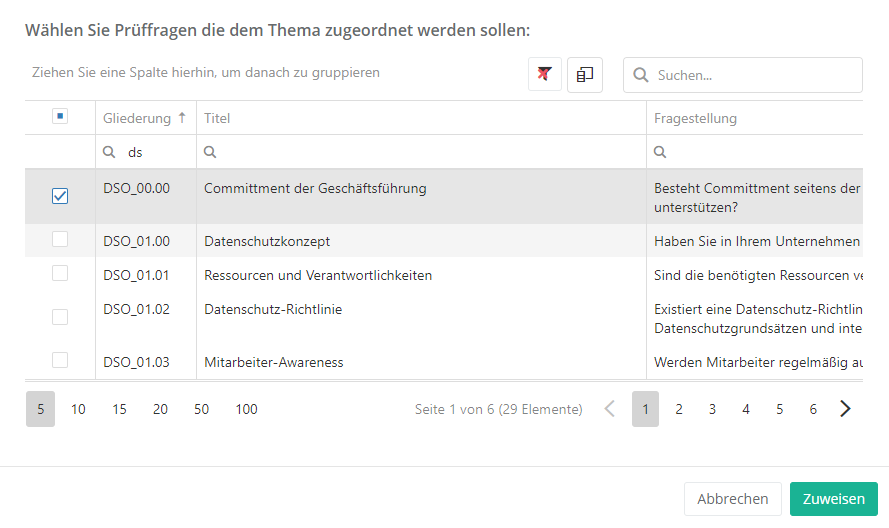
Assign review questions
Once you have created a topic, you need to assign it questions. For this, you may use existing review questions or create new questions. When the question is assigned, you should in turn also assign measures, controls, and threats to the question.
Configure sub-questions
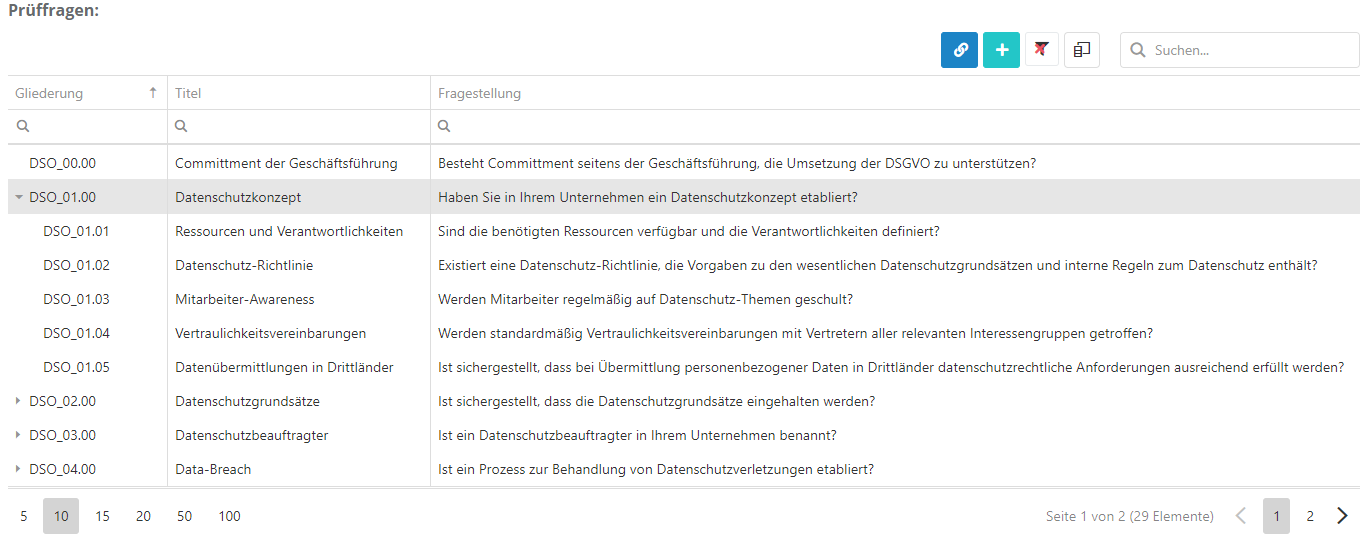
To sort review questions hierarchically, double-click the questions you want to be subordinates and choose a parent question for them (only one layer is supported, meaning a sub-question cannot have further sub-questions). Then, you can choose how the sub-question is to behave depending on the parent question's answer.
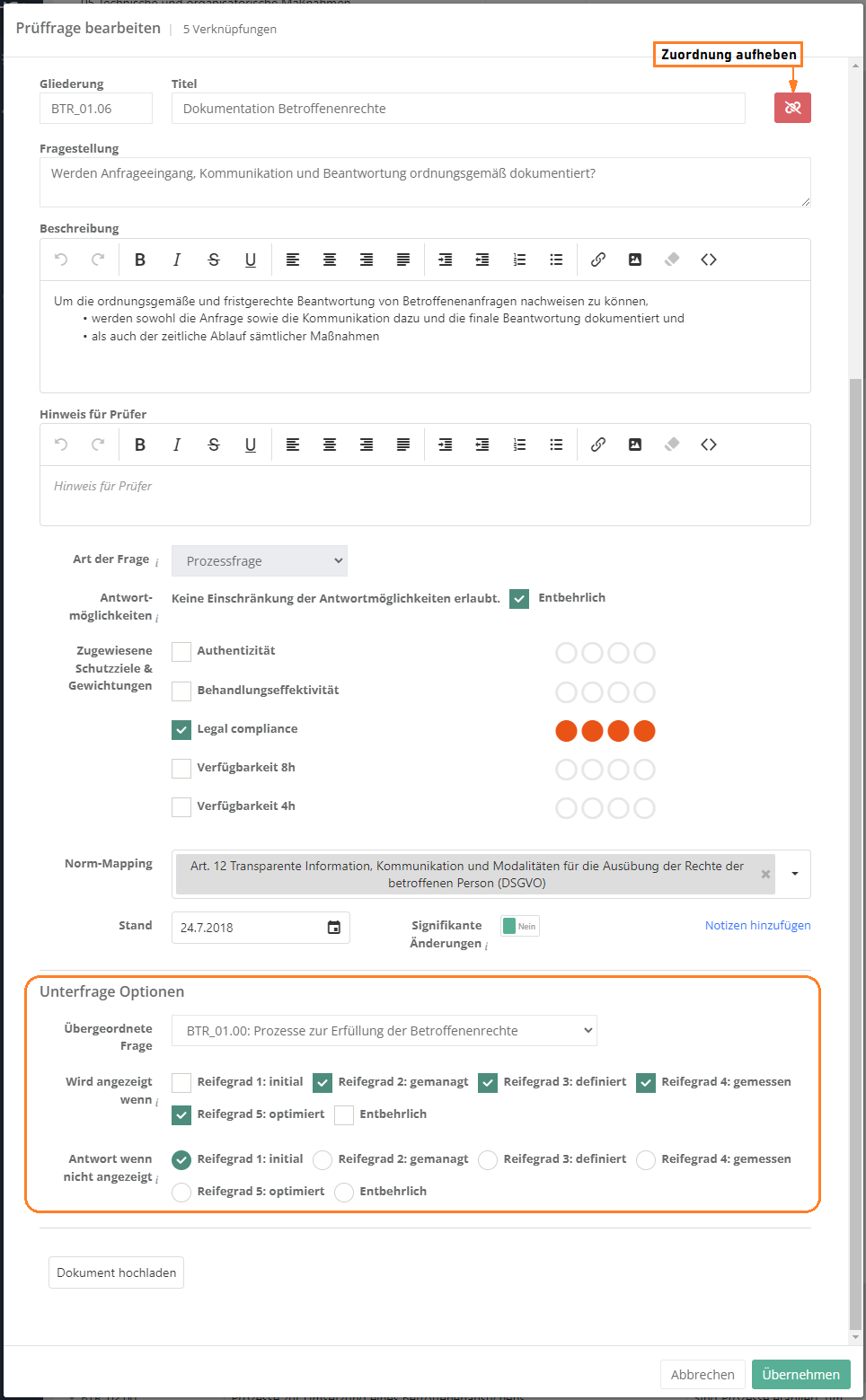
Assign and edit measures, controls, justification templates, and threats
Measures and controls that have been assigned to a review questions are suggested during risk treatment, if their question shows a gap during an assessment. Justification templates can be used as a justification for an answer. If threats are assigned, the question is listed with the threats for analysis purposes.
assign or create:
- The forms for assigning existing measures, controls, justification templates, and threats are the same as the one for assigning review questions, with the exception of the actual content.
- To create see create measure,create control, create justification template und create threat.
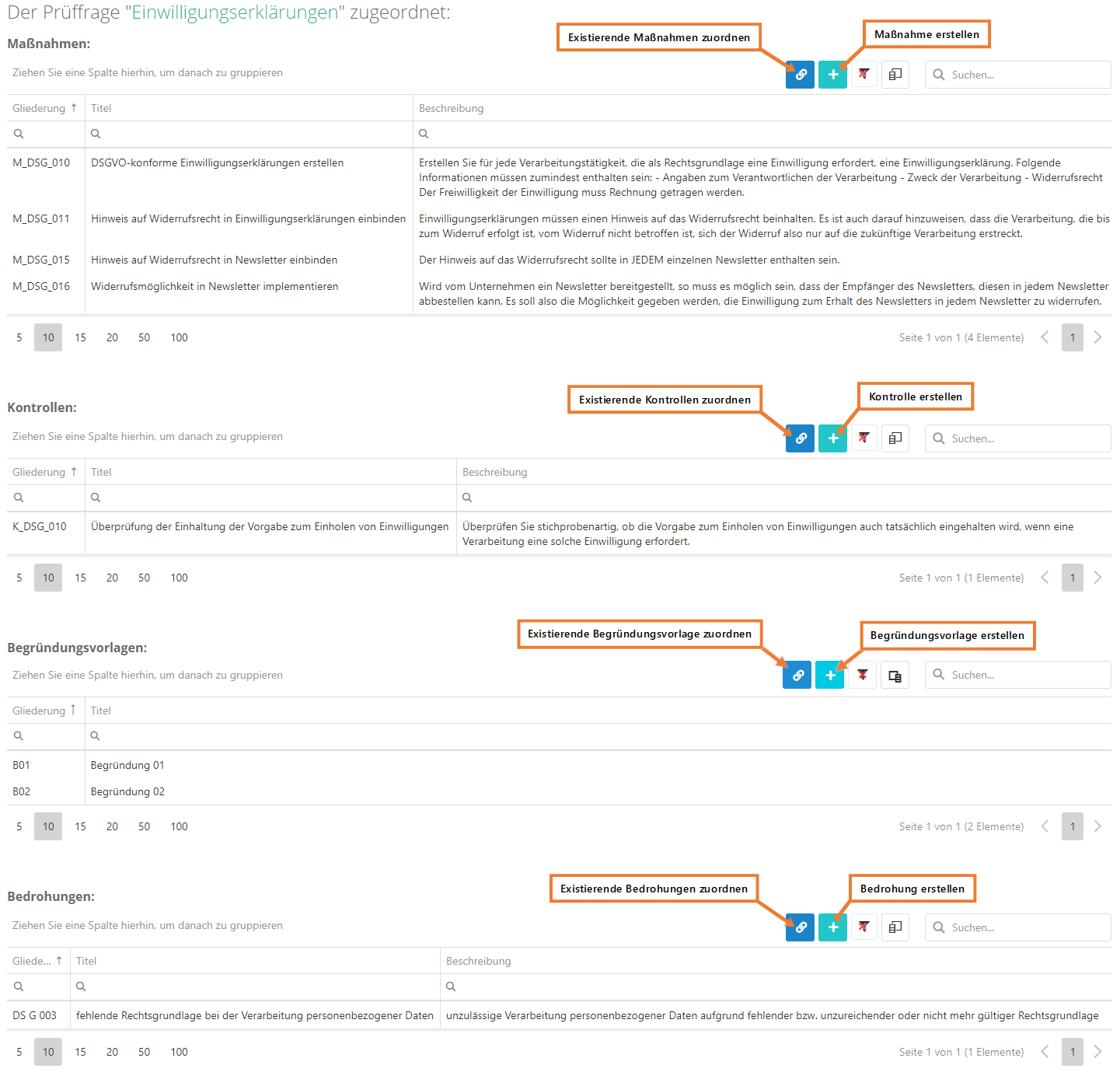
edit and remove assignment:
- As shown above, double-click an element to open its editing interface and edit its properties. Here, you can also remove the assignment to the review question.
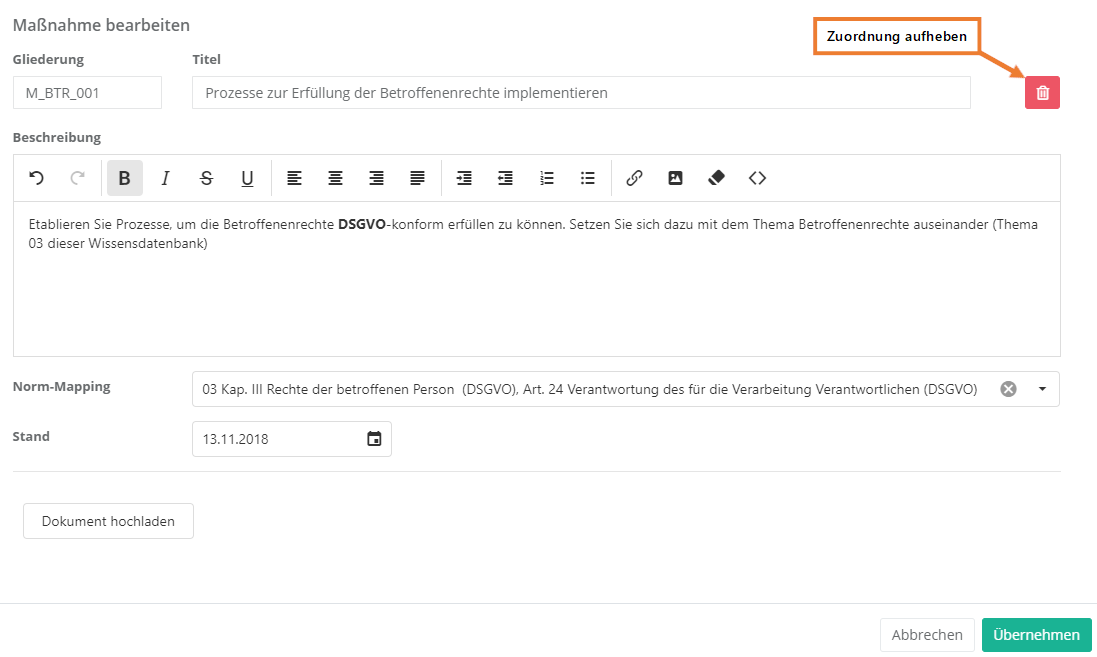
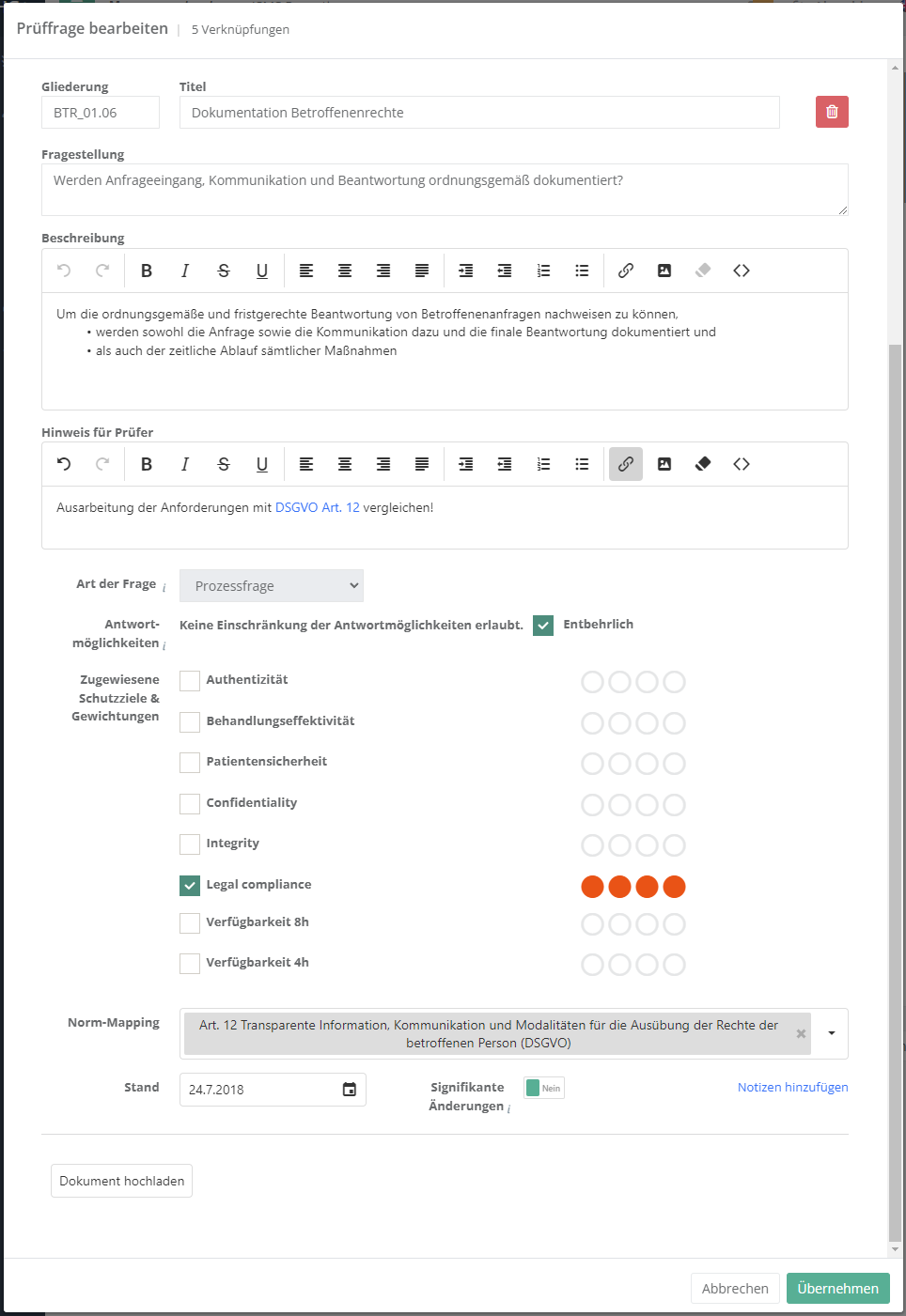
Review question
This tab shows a list of all review questions that exist in the KB. However, they do not show a hierarchy here, this is only displayed under the topics. This tab also lets you create new review questions.
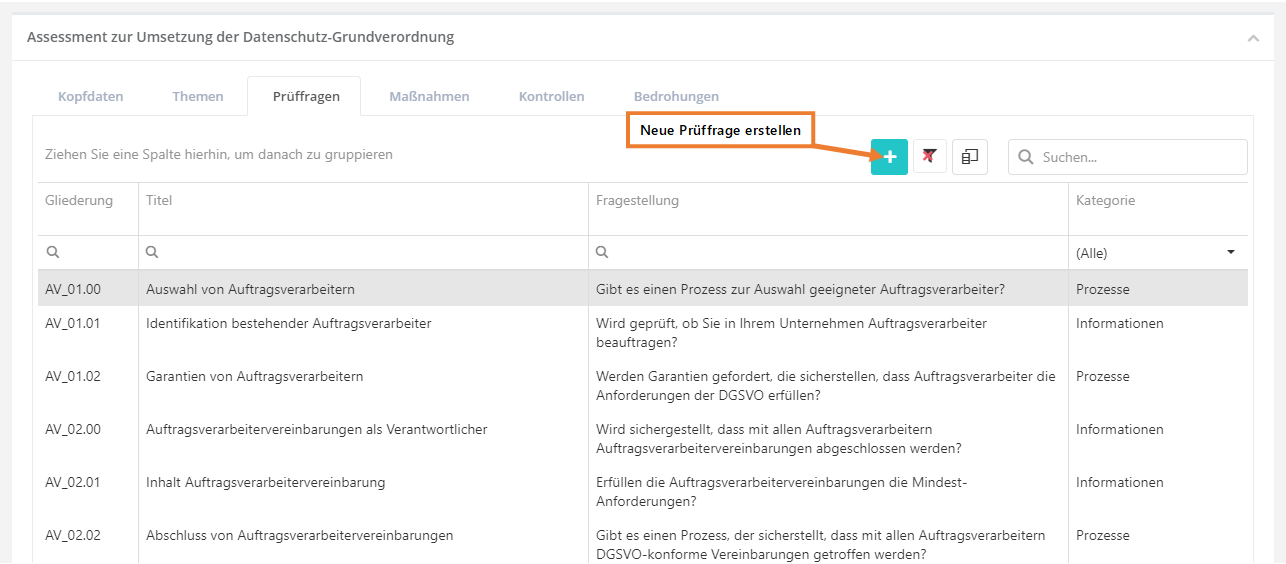
Create, edit, and delete a review question
To create a review question, click the "Create new question" button shown above. To edit or delete a question, double-click the desired question. Then the question can be edited or deleted (via the "trash can" icon). The behaviour of sub-questions can only be changed in the topics tab.
Properties:
- Numbering and title:
- The numbering should be logical and comprehensible, e.g. an abbreviation of the topic and a serial number (DSO_01.00).
The title should be informative, so the user immediately knows what the question is about.
- The numbering should be logical and comprehensible, e.g. an abbreviation of the topic and a serial number (DSO_01.00).
- Question:
- Pose a clearly formulated question here.
- Description:
- If necessary, further describe the question here. For example, you might describe the basic conditions that need to be fulfilled for a question to be answered positively.
NO TRANSLATION
- Hint for auditors:
- Information for auditors can be recorded here. This could, for instance, be links to documents the answers should be compared to, or a checklist with the exam steps.
- This information is only shown in gap analyses that have been opened either in "Risk management → Vulnerabilities" or from an audit. (It is not displayed if the analysis has been opened in the context of "My tasks".)
- Type of question:
- Choose whether it is a technical or a process question. Technical questions are answered with Yes, No, or Partly and process questions with a maturity level.
- Answer types and unnecessary:
- This option allows you to limit the answer types for the question. This is only possible for technical questions. The option "unnecessary" dictates whether a question has to be answered or not. Note that setting a structural question as unnecessary will affect its sub-questions, as their behaviour in response to an unnecessary structural question can be configured.
- Assigned protection targets and weightings:
- Choose, which protection targets are affected if a question reveals a gap.
Example:- Review question about server room security
- Has the door been furnished with a security lock?
- If this question is answered No, major risks concerning confidentiality, integrity, and availability can develop.
- Review question about server room security
- Choose, which protection targets are affected if a question reveals a gap.
Protection target weighting explanation Confidentiality 4 break-in and theft of a hard-drive Availability 4 the burglar could destroy something Integrity 3 The burglar could make changes to a system
- Norm mapping:
- If the question touches one or more norm chapters, this should be recorded here. This allows the creation of a compliance report for a norm.
- Effective date:
- The effective date should be the date of creation or that of the latest revision.
- Author's notes:
- Clicking "Add note" allows the author to record a note for themselves. They could, for example, add to-dos or links to external sources. This information is only visible for the editor of a KB. It has no effect on assessments and is of a purely editorial nature. It is also not exported or imported with a KB.
- External ID:
- With this ID a review question can be updated through an import. For this, the ID needs to match the ID of the review question in the import. This field should only be set manually, if the review question originates in an external system but the questions were created manually before the import and are now to be kept up to date with imports.
Measures
This tab lists all measures in the KB. It also allows the creation of new measures.
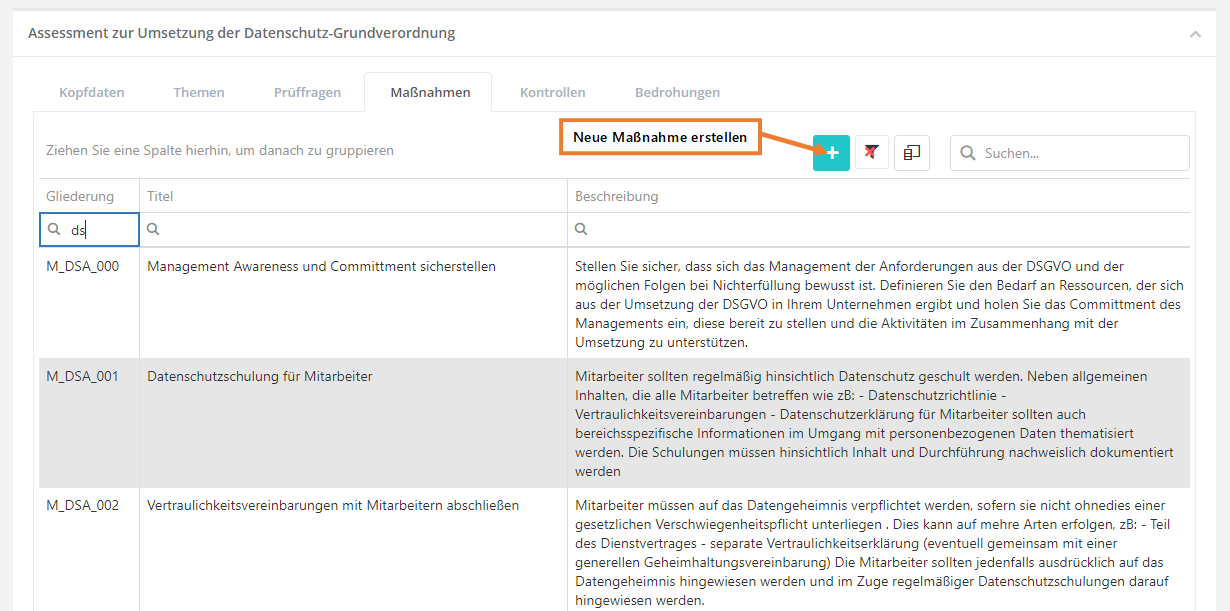
Create, edit, and delete measure
To create a measure, click the "Create new measure" button shown above. To edit or delete a measure, double-click the desired measure. Then the question can be edited or deleted (via the "trash can" icon).
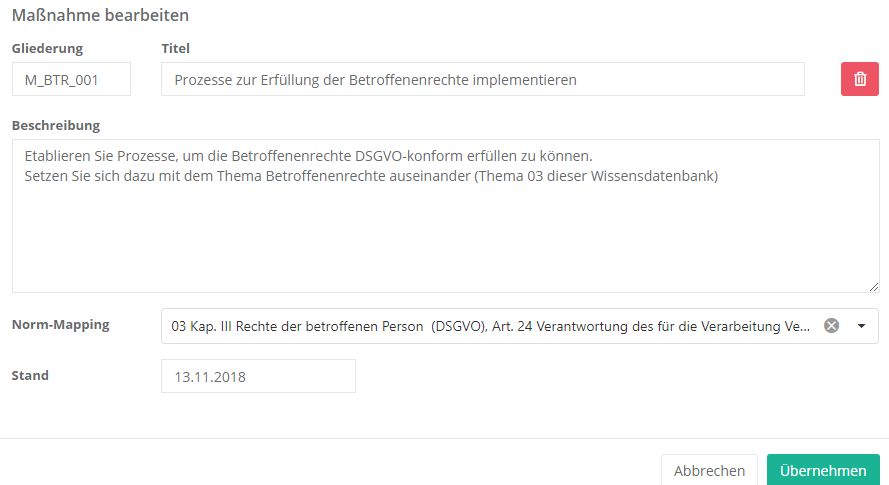
Properties:
- Numbering and title:
- The numbering should be logical and comprehensible.
The title should be informative, so the user immediately knows what the measure is about.
- The numbering should be logical and comprehensible.
- Beschreibung:
- Hier sollten Sie die Maßnahme genauer beschreiben, d.h. erklären Sie was bei der Durchführung der Maßnahme genau zu erledigen ist.
- Norm-Mapping:
- Beschäftigt sich die Frage mit einem oder mehreren Normkapiteln, sollte dies hier eingetragen werden. Daraus lässt sich dann ein Compliance Bericht über die Erfüllung einer Norm erstellen.
- Stand:
- Beim Stand sollten Sie das Erstellungsdatum oder das Datum der letzten Änderung eintragen.
- ID in Drittsystemen:
- Durch diese ID kann die Maßnahme durch einen Import aktualisiert werden. Dafür muss die ID mit der ID der Maßnahme des Imports übereinstimmen. Dieses Feld sollte nur manuell gesetzt werden, falls die Maßnahme eigentlich aus einem Drittsystem stammt, aber die Maßnahme vor einem Import bereits manuell angelegt wurde und die Maßnahme in Zukunft durch Imports aktualisiert werden soll.
Kontrollen
In diesem Reiter werden alle Kontrollen, welche in der WDB existieren aufgelistet. Dieser Reiter bietet auch die Option, neue Kontrollen zu erstellen.
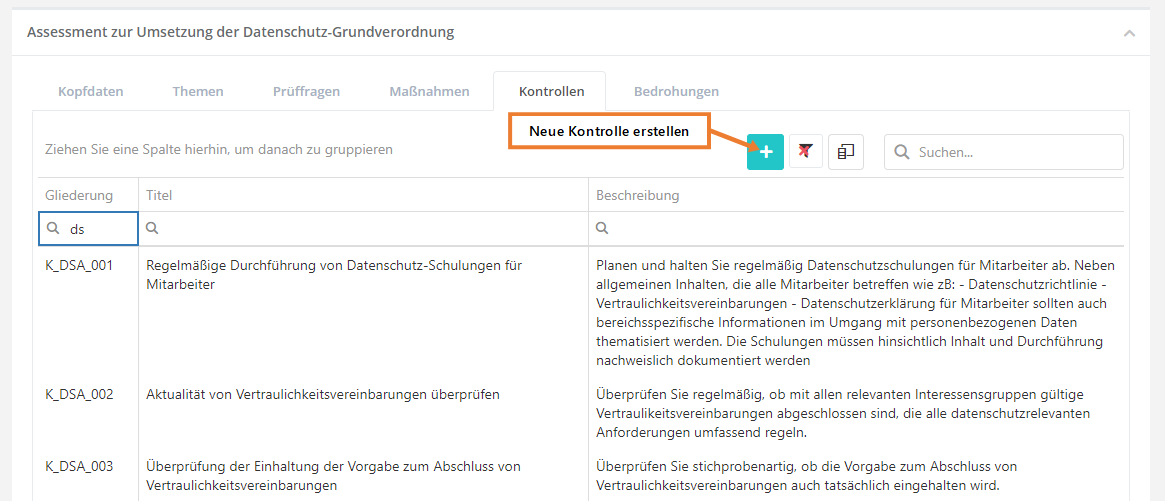
Kontrolle erstellen, bearbeiten und löschen
Um eine Kontrolle zu erstellen, müssen Sie wie im oben gezeigten Screenshot auf den "Neue Kontrolle erstellen" Button klicken. Um eine Kontrolle zu bearbeiten oder zu löschen, müssen Sie auf die gewünschte Kontrolle Doppelklicken. Anschließend kann die Kontrolle über die bearbeiten Maske bearbeitet oder gelöscht werden (löschen über das Mülleimer Symbol).
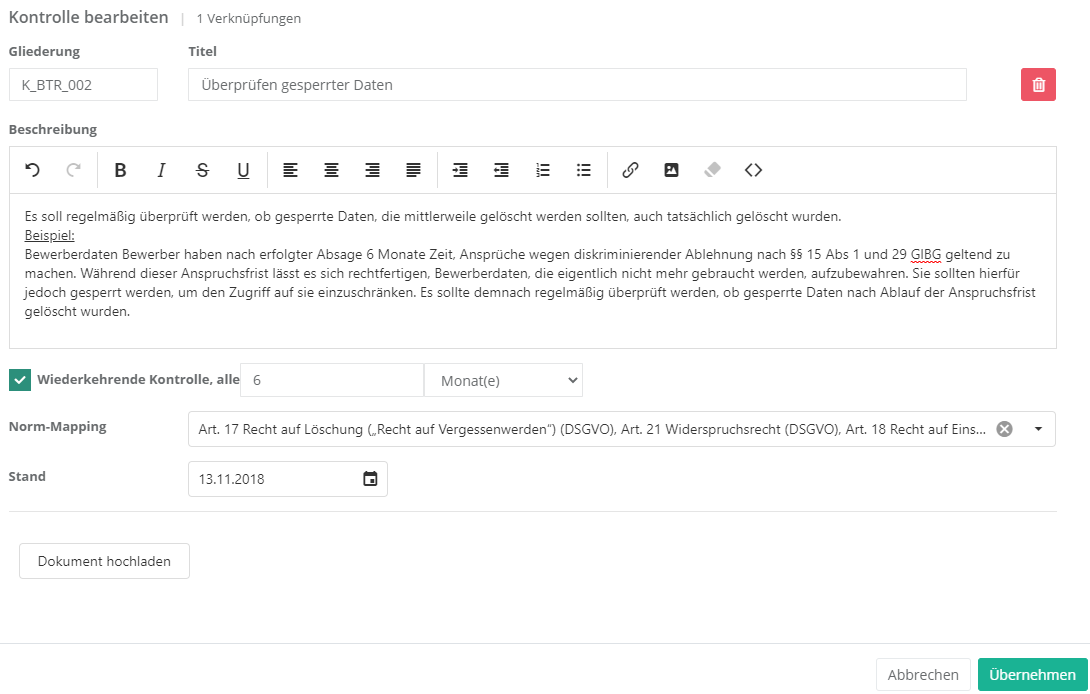
Eigenschaften:
- Gliederung und Titel:
- Die Gliederung sollte logisch und nachvollziehbar gewählt werden.
Der Titel sollte schlagkräftig sein damit klar ist, was die Kontrolle kontrolliert.
- Die Gliederung sollte logisch und nachvollziehbar gewählt werden.
- Beschreibung:
- Hier sollten Sie die Kontrolle genauer beschreiben, d.h. erklären Sie, was bei der Durchführung der Kontrolle genau zu erledigen ist.
- Wiederkehrende Kontrolle:
- Hier kann ein Intervall festgelegt werden, welches dafür sorgt, dass diese Kontrolle alle x Jahre/Monate/etc. durchgeführt werden soll.
- Norm-Mapping:
- Beschäftigt sich die Kontrolle mit einem oder mehreren Normkapiteln, sollte dies hier eingetragen werden. Dadurch lässt sich ein Managementsystem auf Compliance Deckung analysieren.
- Stand:
- Beim Stand sollten Sie das Erstellungsdatum oder das Datum der letzten Änderung eintragen.
- ID in Drittsystemen:
- Durch diese ID kann die Kontrolle durch einen Import aktualisiert werden. Dafür muss die ID mit der ID der Kontrolle des Imports übereinstimmen. Dieses Feld sollte nur manuell gesetzt werden, falls die Kontrolle eigentlich aus einem Drittsystem stammt, aber die Kontrolle vor einem Import bereits manuell angelegt wurde und die Kontrolle in Zukunft durch Imports aktualisiert werden soll.
Begründungsvorlagen
In diesem Reiter werden alle Begründungsvorlagen, welche in der WDB existieren, aufgelistet. Dieser Reiter bietet auch die Option, neue Begründungsvorlagen zu erstellen.
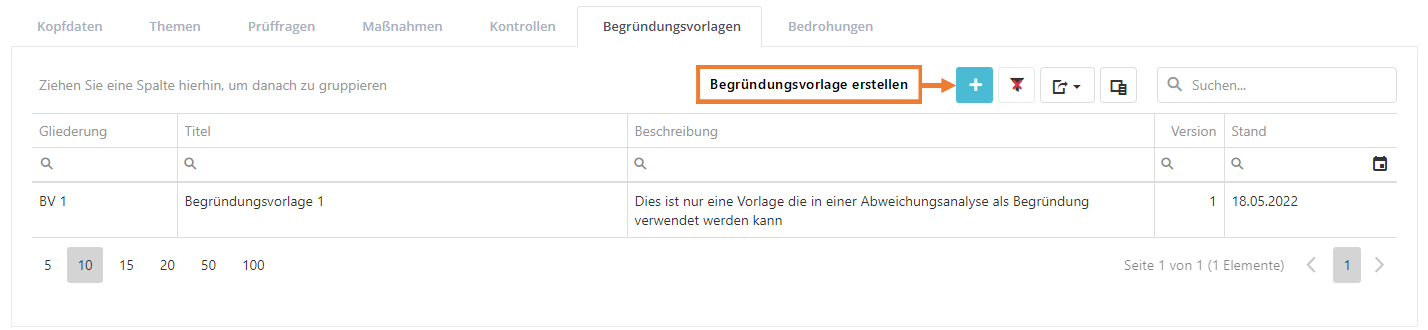
Begründungsvorlage erstellen, bearbeiten und löschen
Um eine Begründungsvorlage zu erstellen, müssen Sie wie im oben gezeigten Screenshot auf den "Neue Begründungsvorlage erstellen" Button klicken. Um eine Begründungsvorlage zu bearbeiten oder zu löschen, müssen Sie auf die gewünschte Begründungsvorlage doppelklicken. Anschließend kann die Begründungsvorlage über die Maske bearbeitet oder gelöscht werden (löschen über das "Mülleimer" Symbol).
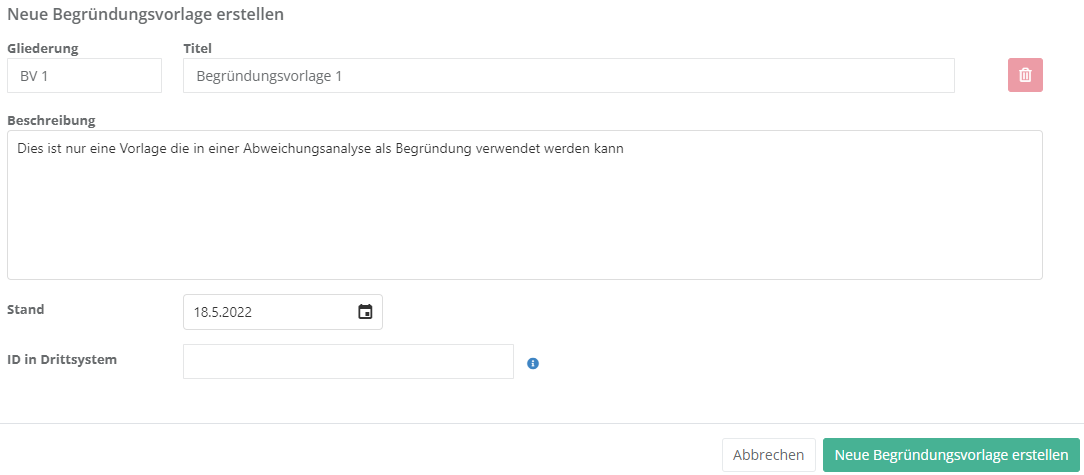
Eigenschaften:
- Gliederung und Titel:
- Die Gliederung sollte logisch und nachvollziehbar gewählt werden.
Der Titel sollte schlagkräftig sein, damit klar ist, welchem Zweck die Begründungsvorlage dient.
- Die Gliederung sollte logisch und nachvollziehbar gewählt werden.
- Beschreibung:
- Hier können Sie einen Text eingeben, der in Abweichungsanalysen als Vorlage für eine Begründung verwendet werden kann.
- Stand:
- Beim Stand sollten Sie das Erstellungsdatum oder das Datum der letzten Änderung eintragen.
- ID in Drittsystemen:
- Durch diese ID kann die Begründungsvorlage durch einen Import aktualisiert werden. Dafür muss die ID mit der ID der Begründungsvorlage des Imports übereinstimmen. Dieses Feld sollte nur manuell gesetzt werden, falls die Begründungsvorlage eigentlich aus einem Drittsystem stammt, aber die Begründungsvorlage vor einem Import bereits manuell angelegt wurde und die Begründungsvorlage in Zukunft durch Imports aktualisiert werden soll.
Bedrohungen
In diesem Reiter werden alle Bedrohungen, welche in der WDB existieren aufgelistet. Dieser Reiter bietet auch die Option, neue Bedrohungen zu erstellen.
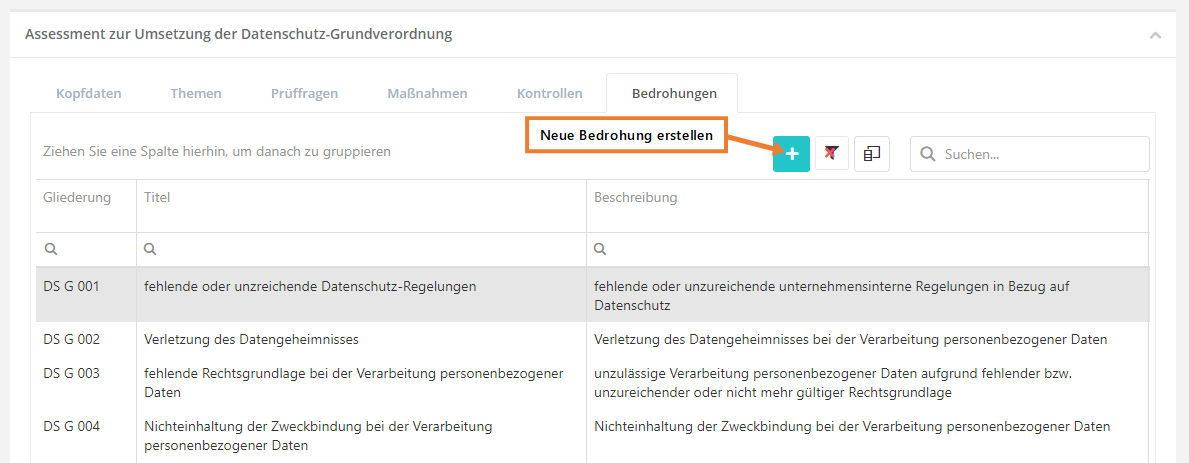
Bedrohung erstellen, bearbeiten und löschen
Um eine Bedrohung zu erstellen, müssen Sie wie im oben gezeigten Screenshot auf den "Neue Bedrohung erstellen" Button klicken. Um eine Bedrohung zu bearbeiten oder zu löschen, müssen Sie auf die gewünschte Bedrohung doppelklicken. Anschließend kann die Bedrohung über die Bearbeiten Maske bearbeitet oder gelöscht werden (löschen über das "Mülleimer" Symbol).
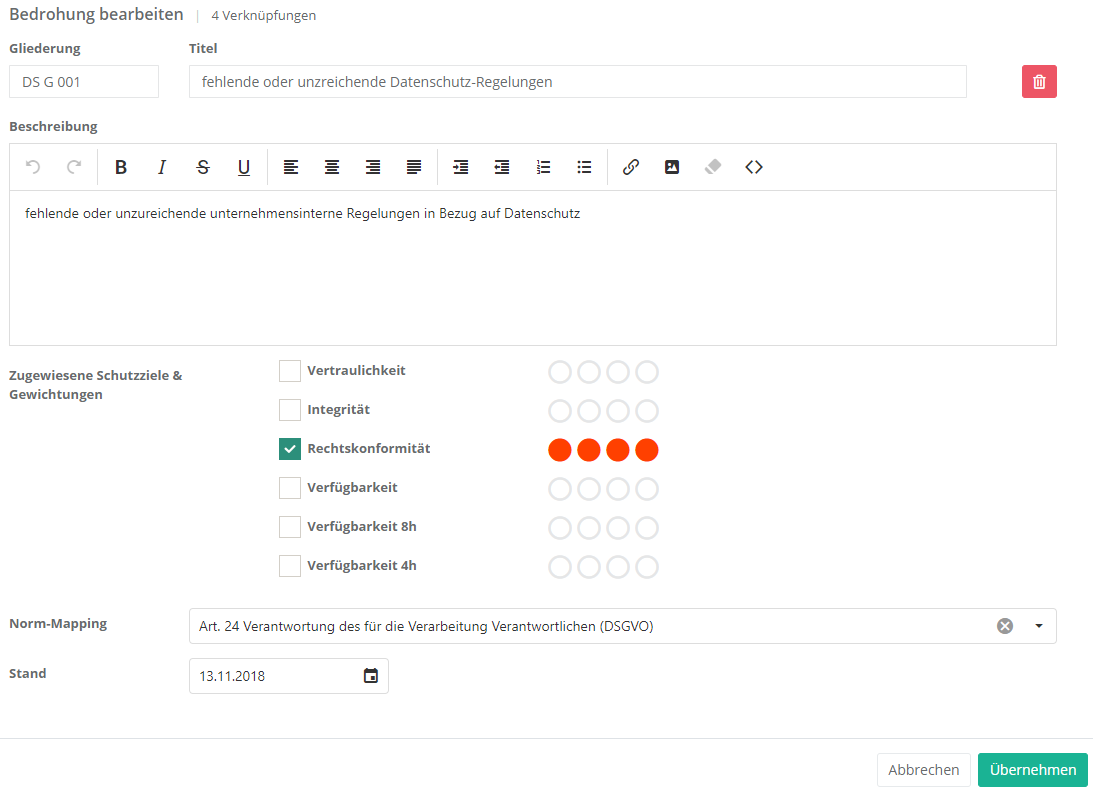
Eigenschaften:
- Gliederung und Titel:
- Die Gliederung sollte logisch und nachvollziehbar gewählt werden.
Der Titel sollte schlagkräftig sein, damit klar ist was die Bedrohung ist, z.B. fehlende oder unzureichende Absicherung bei der Verarbeitung personenbezogener Daten.
- Die Gliederung sollte logisch und nachvollziehbar gewählt werden.
- Beschreibung:
- Hier sollten Sie die Bedrohung genauer beschreiben, d.h. erklären, was genau die Bedrohung ist.
- Zugewiesene Schutzziele und Gewichtungen:
- Hier sollten Sie auswählen, welche Schutzziele betroffen wären, wenn diese Bedrohung auftreten würde.
Beispiel:- Bedrohung Einbruch
- Ein Einbrecher könnte in den Serverraum vordringen, um dort eine Festplatte mit sensiblen Informationen zu entwenden.
- Geschieht dies, können große Schäden im Bereich der Vertraulichkeit, Verfügbarkeit und Integrität entstehen.
- Bedrohung Einbruch
- Hier sollten Sie auswählen, welche Schutzziele betroffen wären, wenn diese Bedrohung auftreten würde.
Schutzziel Gewichtung Erklärung Vertraulichkeit 4 Einbruch und Diebstahl einer Festplatte Verfügbarkeit 4 Der Einbrecher könnte etwas zerstören Integrität 3 Er könnte auch am System etwas ändern
- Norm-Mapping:
- Beschäftigt sich die Bedrohung mit einem oder mehreren Normkapiteln, sollte dies hier eingetragen werden. Daraus lässt sich dann ein Compliance Bericht über die Erfüllung einer Norm erstellen.
- Stand:
- Beim Stand sollten Sie das Erstellungsdatum oder das Datum der letzten Änderung eintragen.
- ID in Drittsystemen:
- Durch diese ID kann die Bedrohung durch einen Import aktualisiert werden. Dafür muss die ID mit der ID der Bedrohung des Imports übereinstimmen. Dieses Feld sollte nur manuell gesetzt werden, falls die Bedrohung eigentlich aus einem Drittsystem stammt, aber die Bedrohung vor einem Import bereits manuell angelegt wurde und die Bedrohung in Zukunft durch Imports aktualisiert werden soll.