Datenimport/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Weitere Optionen
Sala (Diskussion | Beiträge) Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „Data import“ |
Isan (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| (190 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 4 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
With the help of the importer, resources, measures, controls and check questions for knowledge bases or structure updates for organizational units can be imported. These updates can come from an SAP export, for example, or from a specially created Excel or CSV file. In this way, obsolete structures can be updated or completely new structures can be imported. | |||
If an import is performed, all entities that have been changed are updated, and all entities that do not yet exist in HITGuard are created. | |||
== <span id="import"></span> | <span id="Durchführen_eines_Imports"></span> | ||
== <span id="import"></span> Performing an import == | |||
Imports | Imports can be performed only by administrators or experts. | ||
To perform an import, first go to "Administration → <u>Data import</u> | Import logs". All created import configurations are now displayed here. To perform an import, either an existing import configuration is selected from the list or a new import configuration is created - in terms of execution, the processes do not differ. | |||
Each import is documented under "Administration → Data import | <u>Import logs</u>". | |||
To use an existing import configuration, double-click on the desired configuration. | |||
[[Datei:Org import 1.png|left|thumb|900px| | To create a new import configuration, click on the green plus. (see figure) | ||
[[Datei:Org import 1.png|left|thumb|900px|Create new import configuration]] | |||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
Afterwards a mask opens (see figure below), where the name of the configuration has to be set, the type of the configuration has to be selected and the file to be imported has to be uploaded. | |||
The file can be either a CSV file or an Excel file. ([[#Import file structure|Import file structure]]) | |||
[[Datei:Org import 2.png|left|thumb|900px| | [[Datei:Org import 2.png|left|thumb|900px|Select import type]] | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
Clicking on "Next" opens the mask for assigning the fields (see figure below). Here at least all mandatory fields of the selected import type should be assigned. You can find out what these are from the description of the individual imports. | |||
If an Excel file is imported, care must be taken that column headings exist in the file. If these exist, it is selected that the first row contains column headers and should therefore be ignored. | |||
[[Datei:Importer Felder zuordnen.gif|left|thumb|900px|Assign fields]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
If all mandatory fields have now been assigned, the import can be saved and is ready for import. All that remains is to click on "Save and import". | |||
<u>Note</u>: Instead of a username the name of a team can be entered for the field responsible, provided the team was already created in HITGuard. The name must be correct for the import to work. The team is then set as responsible, e.g., for a resource. | |||
[[Datei: | [[Datei:Org import 4.png|left|thumb|901px|Save and import]] | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
If the import was successful, you will see how many entities were newly created and how many were modified. In case of erroneous import operations, those rows and columns that contain errors will be listed for you. | |||
[[Datei:Org import 5.png|left|thumb|900px|Successful organization import]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
<span id="Importprotokolle"></span> | |||
== Import logs == | |||
[[Datei: | Each import attempt is documented under "Administration → Data import | <u>Import logs</u>". Both successful and failed import attempts are recorded. | ||
[[Datei:Importprotokolle Übersicht.png|left|thumb|900px|Overview of the protocols]] | |||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
By double-clicking on an import, you will be redirected to a screen where you can see details such as the reason why the import failed. | |||
[[Datei:Importprotokolle Detailansicht.png|left|thumb|900px|Detail view of an import log]] | |||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
== | <span id="Datenkategorien_importieren"></span> | ||
== Import data categories == | |||
To import data categories, the "Data category" type must be selected during import. | |||
There are two options: | |||
* Create new data categories | |||
* Update existing data categories | |||
Only classes created under Risk Management → Risk Policy → Data Classes are allowed for the Data Class field. | |||
Only the values Yes and No are permitted for the fields Protection needs analysis and Person-related. You determine where the data categories can be used. | |||
For information about responsible persons see [[#ver|User management]]. | |||
<span id="Anlegen_neuer_Datenkategorien"></span> | |||
=== Create new data categories === | |||
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the data set ID in the import file to check whether it already exists anywhere in the HITGuard instance (system-wide) or not. If it does not exist, it is created again. | |||
To create a new data category, you must fill in the mandatory fields | |||
* Record ID ''(system-wide unique identifier)'' | |||
* Name | |||
* Data class (as per the values in Risk Management → Risk policy → Data classes) | |||
must be available and filled in. Only if this is the case, the import is feasible. | |||
Furthermore the fields | |||
* Description | |||
* Parent record ID (parent data category) ''(unique identifier)'' | |||
* Protection needs analysis (Yes/No) | |||
* Personal data (Yes/No) | |||
can be assigned. | |||
If the parent record ID is assigned to a data category, a data category with this ID must either already exist in HITGuard or be created in this import. Furthermore, no cycles may exist. Cycles are used when, for example, data category A has entered data category B as its parent ID and data category B has entered data category A as its parent ID. The importer detects these cycles, prevents the import and refers to the cycle error. | |||
<span id="Aktualisieren_von_Datenkategorien"></span> | |||
=== Update data categories === | |||
If the record ID of the data category is found during the import, no new data category is created, but the existing one is updated. That means: The existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields like e.g. designation, data class or person related. This allows the maintenance of individual data category or larger data category structures . | |||
Example: | |||
:It is decided to create a new data category that should be parent to already existing data categories. In this case, the already existing data categories can be easily subordinated to this new data category by changing their parent ID. | |||
=== Template === | |||
*[[Media:Importvorlage_Datenkategorie.xlsx|Template: Importvorlage Datenkategorie.xlsx]] | |||
<span id="Risiken_importieren"></span> | |||
== Import risks == | |||
To import risks, the "Risk" type is selected during import. | |||
There are two options: | |||
* Create new risk | |||
* Update existing risks | |||
<span id="Anlegen_neuer_Risiken"></span> | |||
=== Creation of new risks=== | |||
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the data set ID in the import file to check whether it already exists anywhere in the HITGuard instance (across management systems) or not. If it does not exist, it is created again. | |||
To create a new risk, you must fill in the mandatory fields | |||
* Record ID ''(unique identifier)'' | |||
* Designation | |||
must be available and filled in. Only if this is the case, the import is possible. | |||
Furthermore, the fields | |||
* Code | |||
* Description | |||
* Probability of occurrence | |||
* Extent of damage | |||
can be assigned. | |||
If the Damage Extent or Probability of Occurrence fields are assigned, then only content that matches the existing HITGuard classes is valid. For more information, see [[Special:MyLanguage/RiskPolicy#prob|Probabilities of occurrence]] or [[Special:MyLanguage/RiskPolicy#Extensions of damage|Extensions of damage]]. | |||
<span id="Aktualisieren_von_Risiken"></span> | |||
=== Updating risks === | |||
If the record ID of the risk is found during the import, no new risk is created, but the existing one is updated. That means: The existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields such as designation, description, responsible person, etc. This enables the maintenance of individual risks. | |||
<u>Caution:</u> The ID of the risk must be distinct across the entire HITGuard installation, it must not repeat in different management systems. If you, for example, import an risk with the ID 1234 into a management system, but in another management system there already is a risk with the ID 1234, then that risk will be overwritten. | |||
=== Template === | |||
* [[Media:Importvorlage_Risiko.xlsx|Template: Importvorlage Risiko.xlsx]] | |||
<span id="Geschäftsprozesse_importieren"></span> | |||
== Import business processes == | |||
To import business processes, the "Business process" type must be selected during import. | |||
There are two options: | |||
* Create new business processes | |||
* Update existing business processes | |||
For information about responsible persons see [[#ver|User management]]. | |||
<span id="Anlegen_neuer_Geschäftsprozesse"></span> | |||
=== Creation of new business processes === | |||
When importing a file, HITGuard checks whether a business process already exists or not based on the record ID in the import file. If none exists, the business process is created. | |||
To create a new business process, you must fill in the mandatory fields | |||
* Record ID ''(system-wide unique identifier)'' | |||
* Name | |||
must be available and filled in. Only if this is the case, the import is possible. | |||
Furthermore the fields | |||
* Code | |||
* Description | |||
* Parent business process record ID ''(system-wide unique identifier)'' | |||
can be assigned. | |||
If the parent business process record ID is assigned, a business process with this ID must either already exist in HITGuard or be created in this import. | |||
Furthermore, no cycles may exist. Cycles exist if, for example, business process A has entered business process B as its parent ID and business process B has entered business process A as its parent ID. The importer recognizes these cycles, prevents the import and refers to the cycle error. | |||
<span id="Aktualisieren_von_Geschäftsprozessen"></span> | |||
=== Update business processes === | |||
If the record ID of the organizational unit is found during the import, no new business process is created, but the existing one is updated. That means: The existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields like description, code, responsible person, or parent record ID. This enables the maintenance of individual business processes or business process structures. | |||
Example: | |||
:It is decided to create a new business process that is parent to already existing business processes. In this case, the already existing business processes can be subordinated to this new business process by changing their parent ID. | |||
=== Template === | |||
* | *[[Media:Importvorlage_Geschäftsprozess.xlsx|Template: Importvorlage Geschäftsprozess.xlsx]] | ||
<span id="Organisationseinheiten_importieren"></span> | |||
== Import organizational units == | |||
To import organizational units, the "Organizational unit" type must be selected during import. | |||
There are two options: | |||
* Create new organizational structures | |||
* Update existing organizational structures | |||
For information about responsible persons see [[#ver|User management]]. | |||
<span id="Anlegen_neuer_Organisationseinheiten/Strukturen"></span> | |||
=== Creation of new organizational units/structures === | |||
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the data set ID in the import file to check whether it already exists or not. If it does not exist, it is created again. | |||
To create a new organizational unit, you must fill in the mandatory fields | |||
* | * Record ID ''(system-wide unique identifier)'' | ||
* Name | |||
must be available and filled in. Only if this is the case, the import is feasible. | |||
* | |||
Furthermore the fields | |||
* Code | |||
* Description | |||
* Parent OU record ID ''(system-wide unique identifier)'' | |||
* Street | |||
* Postal code | |||
* City | |||
* Country | |||
* Sort order | |||
can be assigned. | |||
If the parent OU record ID is assigned, an organizational unit with this ID must either already exist in HITGuard or be created in this import. Furthermore, no cycles may exist. Cycles exist if, for example, organizational unit A has entered organizational unit B as its parent ID and organizational unit B has entered organizational unit A as its parent ID. The importer recognizes these cycles, prevents the import and refers to the cycle error. | |||
<span id="Aktualisieren_von_Organisationseinheiten/Strukturen"></span> | |||
=== Update organizational units/structures === | |||
If the record ID of the organizational unit is found during the import, no new organizational unit is created, but the existing one is updated. That means: The existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields like e.g. country, address or person in charge. This enables the maintenance of individual organizational units or larger organizational structures. | |||
Example: | |||
:It is decided to create a new department that is superior to already existing organizational units. In this case, the already existing organizational units can be subordinated to this new department by changing their parent ID. | |||
== | === Template === | ||
*[[Media:Importvorlage_OrgEh.xlsx|Template: Importvorlage OrgEh.xlsx]] | |||
<span id="Maßnahmen_importieren"></span> | |||
== Import measures == | |||
To import measures, the type "Measure" is selected upon importing. | |||
There are two options: | |||
* Create new measures | |||
* Update existing measures | |||
<span id="Anlegen_neuer_Maßnahmen"></span> | |||
=== Creation of new measures === | |||
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the record ID in the import file to check whether it already exists or not. If it does not exist, it is created again. | |||
To create a new measure, the following mandatory fields must be present and filled in: | |||
* | *Code | ||
* | *OrgUnit (external ID!) | ||
* | *Name | ||
* | *Responsible | ||
*Recognized at | |||
*Record ID<p> | |||
In addition, all prerequisites of the user administration apply if responsible persons are entered (see User administration).<p> | |||
<u>Important</u>: For the organizational unit you need to use its external ID. If you have not yet set this ID, you can do so manually before the import. | |||
Furthermore, the following fields can be added optionally: | |||
*State (0-6, see more information below) | |||
*Description | |||
*Remark | |||
*Budgeted costs | |||
*Actual costs | |||
*Recognized on | |||
*Start date | |||
*Mentioned deadline - Caution: this is a mandatory field if you have configured it under Measures > Settings | |||
*Deadline | |||
*Finished on - Caution: may only be filled in if the measure is imported in the states Completed or Submitted | |||
*Impact - with the names you defined under Measures > Settings | |||
*Effort - with the names you defined under Measures > Settings | |||
*Corrective measure (YES/NO) | |||
*Improvement measure (YES/NO) | |||
*Planned anew (YES/NO) | |||
*Delayed (YES/NO) | |||
*Risk reduction (YES/NO) | |||
*KO-criterion (YES/NO) | |||
= | The digits 0 to 6 are used for the state of the measure: | ||
::{| class="wikitable" | |||
!0 | |||
|Planned | |||
|- | |||
!1 | |||
|Open | |||
|- | |||
!2 | |||
|Suspended | |||
|- | |||
!3 | |||
|Completed (Caution: here the field Completed on must be filled in as well) | |||
|- | |||
!4 | |||
|Cancelled | |||
|- | |||
!5 | |||
|Submitted (here the field Completed on <u>can</u> be filled in) | |||
|- | |||
!6 | |||
|Rejected | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
Note: If you do not enter anything, state 1 (open) is used by default. | |||
<span id="Aktualisieren_von_Maßnahmen"></span> | |||
=== Update measures === | |||
If the record ID of the measure is found during the import, no new measure is created, but the existing one is updated. That is: the existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields. | |||
== | <span id="Vorlage"></span> | ||
=== Template === | |||
*[[Media:Importvorlage_Maßnahmen.xlsx|Template: Importvorlage Maßnahmen.xlsx]] | |||
<span id="Ressourcen_importieren"></span> | |||
== Import resources == | |||
To import resources, the "Resource" type is selected during import. | |||
There are two options: | |||
* Create new resources | |||
* Update existing resources | |||
For information about responsible persons see [[#ver|User management]]. | |||
<span id="Anlegen_neuer_Ressourcen"></span> | |||
=== Create new resources === | |||
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the record ID in the import file to check whether it already exists or not. If it does not exist, it is created again. | |||
To create a new resource, you must fill in the mandatory fields | |||
* Record ID ''(system-wide unique identifier)'' | |||
* and description | |||
must be available and filled in. In addition, all prerequisites of the user administration apply if responsible persons are entered (see User administration). | |||
Furthermore, the fields: | |||
* Description | |||
* model segment | |||
* RTO | |||
* and RPO | |||
can be assigned. In the model segment, the following values are allowed: "Business Service Level", "Application Level", "IT Infrastructure Level", "OT Infrastructure Level", "Physical Security" and "Process Level". If the field is not assigned, the resources are assigned to the model segment "Application Level". RTO and RPO can be imported <u>either</u> as hours or as minutes; hours and minutes cannot be mixed. In that case, the minutes would overwrite the hours.<p><u>Example</u>: If I want an RTO of two and a half hours, I can either enter 2.5 hours or 150 minutes. If I enter 2 hours and 30 minutes, only the 30 minutes will be imported.<p><u>Caution:</u> When mapping the columns you also need to differentiate and decide between hours and minutes. If the field for minutes is available, it will be chosen over the hours, even if it is empty. | |||
[[Datei:Detailansicht_RTORPO_Spaltenzuordnung.png|thumb|900px|left]] <br clear=all> | |||
<span id="Aktualisieren_von_Ressourcen"></span> | |||
=== Update resources === | |||
If the record ID of the resource is found during the import, no new resource is created, but the existing one is updated. That is: the existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields. | |||
=== | <span id="Vorlage"></span> | ||
=== Template === | |||
*[[Media:Importvorlage_Ressourcen.xlsx|Template: Importvorlage Ressource.xlsx]] | |||
<span id="Lieferanten_importieren"></span> | |||
==Import suppliers== | |||
To import suppliers, the "Supplier" type is selected during import. | |||
There are two options: | |||
* Create new suppliers | |||
* Update existing suppliers | |||
=== | <span id="Anlegen_neuer_Lieferanten"></span> | ||
===Create new suppliers=== | |||
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the record ID in the import file to check whether it already exists anywhere in the HITGuard instance (across management systems) or not. If it does not exist, it is created again. | |||
To create a new resource, you must fill in the mandatory fields | |||
* | *Record ID <i>(unique identifier across management systems)</i> | ||
* | *Name. | ||
Only if this is the case, the file can be imported. | |||
Furthermore, the fields | |||
* | *Code | ||
* | *Expiration date | ||
*Deactivated (x for yes, empty for no; true/false) | |||
*External metric | |||
*Justification | |||
*Street | |||
*Post code | |||
*City | |||
*County | |||
*Country | |||
*E-mail | |||
*Telephone | |||
*Homepage | |||
can be present and filled in. | |||
=== | <span id="Aktualisieren_von_Lieferanten"></span> | ||
===Update suppliers=== | |||
If the record ID of the supplier is found during the import, no new supplier is created, but the existing one is updated. That means: The existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields such as name, description, expiration date, etc. This enables the maintenance of individual suppliers. | |||
=== | <span id="Vorlage"></span> | ||
===Template=== | |||
*[[Media: | *[[Media:Importvorlage_Lieferanten_(1).xlsx|Template: Importvorlage Lieferanten.xlsx]] | ||
== | <span id="Elemente_für_Wissensdatenbanken_(WDBs)_importieren"></span> | ||
== Import knowledge base (KB) elements == | |||
The importer offers the possibility to import measures, controls, review questions, and/or justification templates into an existing knowledge base. For this purpose, the type "WDB" is selected for the importer. Then, the knowledge base into which the measures, controls, review questions, or justification templates are to be imported is specified. This must be a knowledge base that has not been published. | |||
In order to import measures, controls, review questions, and/or justification templates, the fields | |||
* Title | |||
* Record ID ''(unique identifier)'' | |||
must be assigned. | |||
<b>Caution:</b> If the record ID already exists in the KB, no new record is created, but the old one is updated. | |||
Furthermore, in all tabs there are the fields: | |||
* | * Outline | ||
* | * Description | ||
* Status: ''(Date value)'' | |||
In the Question tab, there are also the fields: | |||
* Question | |||
* Type of question : This defines the type of the review question. Allowed values of the field are: "process question" or "technical question" or "information gathering". Process questions can be answered with a score from 1-5 according to the evaluation schema, technical questions with Yes/No/Partial, and information gatherings are answered by filling in the comment and/or uploading an attachment. If the column is not filled, all review questions will be imported as technical questions. | |||
''' | '''Note:''' For an import, columns from all three tabs do not have to be assigned. So you can import review questions, measures, controls, or justification templates separately. | ||
=== | <span id="Vorlagen"></span> | ||
=== Templates === | |||
*[[Media: | *[[Media:Importvorlage_WDB_Prüffrage.xlsx|Template: Importvorlage WDB Prüffrage.xslx]] | ||
*[[Media: | *[[Media:Importvorlage_WDB_Maßnahme.xlsx|Template: Importvorlage WDB Maßnahme.xslx]] | ||
*[[Media: | *[[Media:Importvorlage_WDB_Kontrolle.xlsx|Template: Importvorlage WDB Kontrolle.xslx]] | ||
*[[Media: | *[[Media:Importvorlage_WDB_PF-M-K.xlsx|Template: Importvorlage WDB Prüffrage, Maßnahme und Kontrolle.xslx]] | ||
== <span id=ver></span> | <span id="Benutzerverwaltung"></span> | ||
== <span id=ver></span>User management == | |||
When importing organizational units, data categories and resources, a responsible person can optionally be specified. | |||
If only the user name is specified, the responsible person is assigned, but not modified. Therefore, the user must already exist. In the "Responsible" tab, all fields except for the user name can be ignored in this case.<p>However, with the help of the importer it is also possible to update or create users. | |||
=== | <span id="Anlage_eines_neuen_Benutzers"></span> | ||
=== Creation of a new user === | |||
If a responsible person is entered during import that has not yet been created in HITGuard, there are two variants of how HITGuard handles this: | |||
# Active Directory Integration | # Active Directory Integration is disabled: | ||
#: | #: | ||
#: | #: The user is created completely new, so that this can be performed, the mandatory fields of the responsible person must be present and entered in the import file. These are: | ||
#::* | #::* Username | ||
#::* E- | #::* E-mail | ||
#::* | #::* Password (between 12 and 20 characters, with at least 3 of the 4 criteria special characters, upper case, lower case and digits) | ||
#: [[Datei:Verantwortlichen import 1.png|left|thumb|900px| | #: [[Datei:Verantwortlichen import 1.png|left|thumb|900px|mandatory fields when creating a new user]]<br clear=all> | ||
# Active Directory | # Active Directory integration is enabled: | ||
#: | #: | ||
#: | #: If Active Directory Integration is enabled, only users that exist in Active Directory can be created. However, the first name, last name and email fields can still be assigned. This means that it is possible to change the user's data during import and thus add or correct any errors or information from the Active Directory that is not maintained in HITGuard. | ||
=== | <span id="Aktualisieren_von_Benutzern"></span> | ||
=== Update users === | |||
It is possible to update users with the help of the importer. This is useful, for example, if the e-mail or last name of a user changes. The importer checks at each import, if a user is entered, if additional fields like e-mail, last name, etc. exist in the import file, if yes, the content of these fields will be updated with the new content. | |||
This makes it possible to keep information in HITGuard about users that do not exist or are not maintained in the Active Directory. It should be noted that HITGuard does not update the Active Directory! | |||
==== | <span id="Deaktivierte_Benutzer"></span> | ||
==== Deactivated users ==== | |||
If a deactivated user is entered or updated as the responsible person during an update, this user is not activated as a result, i.e. he does not change status. However, he will be updated and entered as the responsible person. | |||
== | <span id="Aufbau_einer_Importdatei"></span> | ||
== Structure of an import file == | |||
The importer supports two format types: | |||
* CSV | * CSV | ||
* Excel | * Excel files | ||
=== Excel === | === Excel === | ||
The structure of an Excel file consists of a table in which all relevant data is represented as a column in a table. Each row corresponds e.g. to a new organizational unit or other structure to be imported. During import, depending on the structure, the first row can or must be skipped if this row is the column header. | |||
[[Datei:Excel org import example.PNG|left|thumb|900px| | [[Datei:Excel org import example.PNG|left|thumb|900px|Example of an Excel import]] | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
=== CSV === | === CSV === | ||
The structure of a CSV file usually consists of one line, in which the column headings are separated by semicolons. Each additional line contains information about the structure to be imported. It is important that each line has the same number of columns (i.e. the same number of semicolons). Depending on the structure, the first line can or must be skipped during the import if this line contains the column headings. | |||
[[Datei:Csv org import example.PNG|left|thumb|701px| | [[Datei:Csv org import example.PNG|left|thumb|701px|Example of CSV importt]] | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 28. Oktober 2025, 10:20 Uhr
With the help of the importer, resources, measures, controls and check questions for knowledge bases or structure updates for organizational units can be imported. These updates can come from an SAP export, for example, or from a specially created Excel or CSV file. In this way, obsolete structures can be updated or completely new structures can be imported.
If an import is performed, all entities that have been changed are updated, and all entities that do not yet exist in HITGuard are created.
Performing an import
Imports can be performed only by administrators or experts.
To perform an import, first go to "Administration → Data import | Import logs". All created import configurations are now displayed here. To perform an import, either an existing import configuration is selected from the list or a new import configuration is created - in terms of execution, the processes do not differ.
Each import is documented under "Administration → Data import | Import logs".
To use an existing import configuration, double-click on the desired configuration.
To create a new import configuration, click on the green plus. (see figure)

Afterwards a mask opens (see figure below), where the name of the configuration has to be set, the type of the configuration has to be selected and the file to be imported has to be uploaded.
The file can be either a CSV file or an Excel file. (Import file structure)

Clicking on "Next" opens the mask for assigning the fields (see figure below). Here at least all mandatory fields of the selected import type should be assigned. You can find out what these are from the description of the individual imports.
If an Excel file is imported, care must be taken that column headings exist in the file. If these exist, it is selected that the first row contains column headers and should therefore be ignored.

If all mandatory fields have now been assigned, the import can be saved and is ready for import. All that remains is to click on "Save and import".
Note: Instead of a username the name of a team can be entered for the field responsible, provided the team was already created in HITGuard. The name must be correct for the import to work. The team is then set as responsible, e.g., for a resource.

If the import was successful, you will see how many entities were newly created and how many were modified. In case of erroneous import operations, those rows and columns that contain errors will be listed for you.

Import logs
Each import attempt is documented under "Administration → Data import | Import logs". Both successful and failed import attempts are recorded.

By double-clicking on an import, you will be redirected to a screen where you can see details such as the reason why the import failed.

Import data categories
To import data categories, the "Data category" type must be selected during import.
There are two options:
- Create new data categories
- Update existing data categories
Only classes created under Risk Management → Risk Policy → Data Classes are allowed for the Data Class field.
Only the values Yes and No are permitted for the fields Protection needs analysis and Person-related. You determine where the data categories can be used.
For information about responsible persons see User management.
Create new data categories
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the data set ID in the import file to check whether it already exists anywhere in the HITGuard instance (system-wide) or not. If it does not exist, it is created again.
To create a new data category, you must fill in the mandatory fields
- Record ID (system-wide unique identifier)
- Name
- Data class (as per the values in Risk Management → Risk policy → Data classes)
must be available and filled in. Only if this is the case, the import is feasible.
Furthermore the fields
- Description
- Parent record ID (parent data category) (unique identifier)
- Protection needs analysis (Yes/No)
- Personal data (Yes/No)
can be assigned.
If the parent record ID is assigned to a data category, a data category with this ID must either already exist in HITGuard or be created in this import. Furthermore, no cycles may exist. Cycles are used when, for example, data category A has entered data category B as its parent ID and data category B has entered data category A as its parent ID. The importer detects these cycles, prevents the import and refers to the cycle error.
Update data categories
If the record ID of the data category is found during the import, no new data category is created, but the existing one is updated. That means: The existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields like e.g. designation, data class or person related. This allows the maintenance of individual data category or larger data category structures .
Example:
- It is decided to create a new data category that should be parent to already existing data categories. In this case, the already existing data categories can be easily subordinated to this new data category by changing their parent ID.
Template
Import risks
To import risks, the "Risk" type is selected during import.
There are two options:
- Create new risk
- Update existing risks
Creation of new risks
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the data set ID in the import file to check whether it already exists anywhere in the HITGuard instance (across management systems) or not. If it does not exist, it is created again.
To create a new risk, you must fill in the mandatory fields
- Record ID (unique identifier)
- Designation
must be available and filled in. Only if this is the case, the import is possible.
Furthermore, the fields
- Code
- Description
- Probability of occurrence
- Extent of damage
can be assigned.
If the Damage Extent or Probability of Occurrence fields are assigned, then only content that matches the existing HITGuard classes is valid. For more information, see Probabilities of occurrence or Extensions of damage.
Updating risks
If the record ID of the risk is found during the import, no new risk is created, but the existing one is updated. That means: The existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields such as designation, description, responsible person, etc. This enables the maintenance of individual risks.
Caution: The ID of the risk must be distinct across the entire HITGuard installation, it must not repeat in different management systems. If you, for example, import an risk with the ID 1234 into a management system, but in another management system there already is a risk with the ID 1234, then that risk will be overwritten.
Template
Import business processes
To import business processes, the "Business process" type must be selected during import.
There are two options:
- Create new business processes
- Update existing business processes
For information about responsible persons see User management.
Creation of new business processes
When importing a file, HITGuard checks whether a business process already exists or not based on the record ID in the import file. If none exists, the business process is created.
To create a new business process, you must fill in the mandatory fields
- Record ID (system-wide unique identifier)
- Name
must be available and filled in. Only if this is the case, the import is possible.
Furthermore the fields
- Code
- Description
- Parent business process record ID (system-wide unique identifier)
can be assigned.
If the parent business process record ID is assigned, a business process with this ID must either already exist in HITGuard or be created in this import. Furthermore, no cycles may exist. Cycles exist if, for example, business process A has entered business process B as its parent ID and business process B has entered business process A as its parent ID. The importer recognizes these cycles, prevents the import and refers to the cycle error.
Update business processes
If the record ID of the organizational unit is found during the import, no new business process is created, but the existing one is updated. That means: The existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields like description, code, responsible person, or parent record ID. This enables the maintenance of individual business processes or business process structures.
Example:
- It is decided to create a new business process that is parent to already existing business processes. In this case, the already existing business processes can be subordinated to this new business process by changing their parent ID.
Template
Import organizational units
To import organizational units, the "Organizational unit" type must be selected during import.
There are two options:
- Create new organizational structures
- Update existing organizational structures
For information about responsible persons see User management.
Creation of new organizational units/structures
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the data set ID in the import file to check whether it already exists or not. If it does not exist, it is created again.
To create a new organizational unit, you must fill in the mandatory fields
- Record ID (system-wide unique identifier)
- Name
must be available and filled in. Only if this is the case, the import is feasible.
Furthermore the fields
- Code
- Description
- Parent OU record ID (system-wide unique identifier)
- Street
- Postal code
- City
- Country
- Sort order
can be assigned.
If the parent OU record ID is assigned, an organizational unit with this ID must either already exist in HITGuard or be created in this import. Furthermore, no cycles may exist. Cycles exist if, for example, organizational unit A has entered organizational unit B as its parent ID and organizational unit B has entered organizational unit A as its parent ID. The importer recognizes these cycles, prevents the import and refers to the cycle error.
Update organizational units/structures
If the record ID of the organizational unit is found during the import, no new organizational unit is created, but the existing one is updated. That means: The existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields like e.g. country, address or person in charge. This enables the maintenance of individual organizational units or larger organizational structures.
Example:
- It is decided to create a new department that is superior to already existing organizational units. In this case, the already existing organizational units can be subordinated to this new department by changing their parent ID.
Template
Import measures
To import measures, the type "Measure" is selected upon importing.
There are two options:
- Create new measures
- Update existing measures
Creation of new measures
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the record ID in the import file to check whether it already exists or not. If it does not exist, it is created again.
To create a new measure, the following mandatory fields must be present and filled in:
- Code
- OrgUnit (external ID!)
- Name
- Responsible
- Recognized at
- Record ID
In addition, all prerequisites of the user administration apply if responsible persons are entered (see User administration).
Important: For the organizational unit you need to use its external ID. If you have not yet set this ID, you can do so manually before the import. Furthermore, the following fields can be added optionally:
- State (0-6, see more information below)
- Description
- Remark
- Budgeted costs
- Actual costs
- Recognized on
- Start date
- Mentioned deadline - Caution: this is a mandatory field if you have configured it under Measures > Settings
- Deadline
- Finished on - Caution: may only be filled in if the measure is imported in the states Completed or Submitted
- Impact - with the names you defined under Measures > Settings
- Effort - with the names you defined under Measures > Settings
- Corrective measure (YES/NO)
- Improvement measure (YES/NO)
- Planned anew (YES/NO)
- Delayed (YES/NO)
- Risk reduction (YES/NO)
- KO-criterion (YES/NO)
The digits 0 to 6 are used for the state of the measure:
0 Planned 1 Open 2 Suspended 3 Completed (Caution: here the field Completed on must be filled in as well) 4 Cancelled 5 Submitted (here the field Completed on can be filled in) 6 Rejected
Note: If you do not enter anything, state 1 (open) is used by default.
Update measures
If the record ID of the measure is found during the import, no new measure is created, but the existing one is updated. That is: the existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields.
Template
Import resources
To import resources, the "Resource" type is selected during import.
There are two options:
- Create new resources
- Update existing resources
For information about responsible persons see User management.
Create new resources
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the record ID in the import file to check whether it already exists or not. If it does not exist, it is created again.
To create a new resource, you must fill in the mandatory fields
- Record ID (system-wide unique identifier)
- and description
must be available and filled in. In addition, all prerequisites of the user administration apply if responsible persons are entered (see User administration).
Furthermore, the fields:
- Description
- model segment
- RTO
- and RPO
can be assigned. In the model segment, the following values are allowed: "Business Service Level", "Application Level", "IT Infrastructure Level", "OT Infrastructure Level", "Physical Security" and "Process Level". If the field is not assigned, the resources are assigned to the model segment "Application Level". RTO and RPO can be imported either as hours or as minutes; hours and minutes cannot be mixed. In that case, the minutes would overwrite the hours.
Example: If I want an RTO of two and a half hours, I can either enter 2.5 hours or 150 minutes. If I enter 2 hours and 30 minutes, only the 30 minutes will be imported.
Caution: When mapping the columns you also need to differentiate and decide between hours and minutes. If the field for minutes is available, it will be chosen over the hours, even if it is empty.
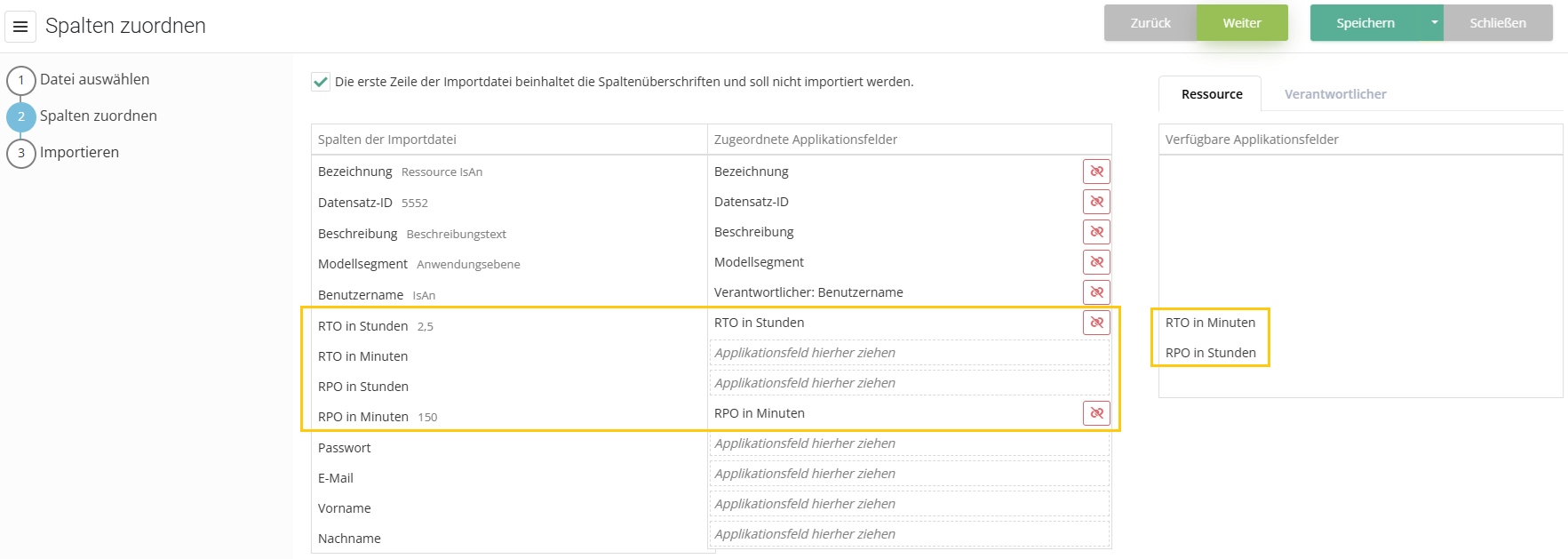
Update resources
If the record ID of the resource is found during the import, no new resource is created, but the existing one is updated. That is: the existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields.
Template
Import suppliers
To import suppliers, the "Supplier" type is selected during import.
There are two options:
- Create new suppliers
- Update existing suppliers
Create new suppliers
When importing a file, HITGuard uses the record ID in the import file to check whether it already exists anywhere in the HITGuard instance (across management systems) or not. If it does not exist, it is created again.
To create a new resource, you must fill in the mandatory fields
- Record ID (unique identifier across management systems)
- Name.
Only if this is the case, the file can be imported.
Furthermore, the fields
- Code
- Expiration date
- Deactivated (x for yes, empty for no; true/false)
- External metric
- Justification
- Street
- Post code
- City
- County
- Country
- Telephone
- Homepage
can be present and filled in.
Update suppliers
If the record ID of the supplier is found during the import, no new supplier is created, but the existing one is updated. That means: The existing fields of the import file update the already existing fields such as name, description, expiration date, etc. This enables the maintenance of individual suppliers.
Template
Import knowledge base (KB) elements
The importer offers the possibility to import measures, controls, review questions, and/or justification templates into an existing knowledge base. For this purpose, the type "WDB" is selected for the importer. Then, the knowledge base into which the measures, controls, review questions, or justification templates are to be imported is specified. This must be a knowledge base that has not been published.
In order to import measures, controls, review questions, and/or justification templates, the fields
- Title
- Record ID (unique identifier)
must be assigned.
Caution: If the record ID already exists in the KB, no new record is created, but the old one is updated.
Furthermore, in all tabs there are the fields:
- Outline
- Description
- Status: (Date value)
In the Question tab, there are also the fields:
- Question
- Type of question : This defines the type of the review question. Allowed values of the field are: "process question" or "technical question" or "information gathering". Process questions can be answered with a score from 1-5 according to the evaluation schema, technical questions with Yes/No/Partial, and information gatherings are answered by filling in the comment and/or uploading an attachment. If the column is not filled, all review questions will be imported as technical questions.
Note: For an import, columns from all three tabs do not have to be assigned. So you can import review questions, measures, controls, or justification templates separately.
Templates
- Template: Importvorlage WDB Prüffrage.xslx
- Template: Importvorlage WDB Maßnahme.xslx
- Template: Importvorlage WDB Kontrolle.xslx
- Template: Importvorlage WDB Prüffrage, Maßnahme und Kontrolle.xslx
User management
When importing organizational units, data categories and resources, a responsible person can optionally be specified.
If only the user name is specified, the responsible person is assigned, but not modified. Therefore, the user must already exist. In the "Responsible" tab, all fields except for the user name can be ignored in this case.
However, with the help of the importer it is also possible to update or create users.
Creation of a new user
If a responsible person is entered during import that has not yet been created in HITGuard, there are two variants of how HITGuard handles this:
- Active Directory Integration is disabled:
- The user is created completely new, so that this can be performed, the mandatory fields of the responsible person must be present and entered in the import file. These are:
- Username
- Password (between 12 and 20 characters, with at least 3 of the 4 criteria special characters, upper case, lower case and digits)

mandatory fields when creating a new user
- The user is created completely new, so that this can be performed, the mandatory fields of the responsible person must be present and entered in the import file. These are:
- Active Directory integration is enabled:
- If Active Directory Integration is enabled, only users that exist in Active Directory can be created. However, the first name, last name and email fields can still be assigned. This means that it is possible to change the user's data during import and thus add or correct any errors or information from the Active Directory that is not maintained in HITGuard.
Update users
It is possible to update users with the help of the importer. This is useful, for example, if the e-mail or last name of a user changes. The importer checks at each import, if a user is entered, if additional fields like e-mail, last name, etc. exist in the import file, if yes, the content of these fields will be updated with the new content.
This makes it possible to keep information in HITGuard about users that do not exist or are not maintained in the Active Directory. It should be noted that HITGuard does not update the Active Directory!
Deactivated users
If a deactivated user is entered or updated as the responsible person during an update, this user is not activated as a result, i.e. he does not change status. However, he will be updated and entered as the responsible person.
Structure of an import file
The importer supports two format types:
- CSV
- Excel files
Excel
The structure of an Excel file consists of a table in which all relevant data is represented as a column in a table. Each row corresponds e.g. to a new organizational unit or other structure to be imported. During import, depending on the structure, the first row can or must be skipped if this row is the column header.

CSV
The structure of a CSV file usually consists of one line, in which the column headings are separated by semicolons. Each additional line contains information about the structure to be imported. It is important that each line has the same number of columns (i.e. the same number of semicolons). Depending on the structure, the first line can or must be skipped during the import if this line contains the column headings.
